Figure 1.
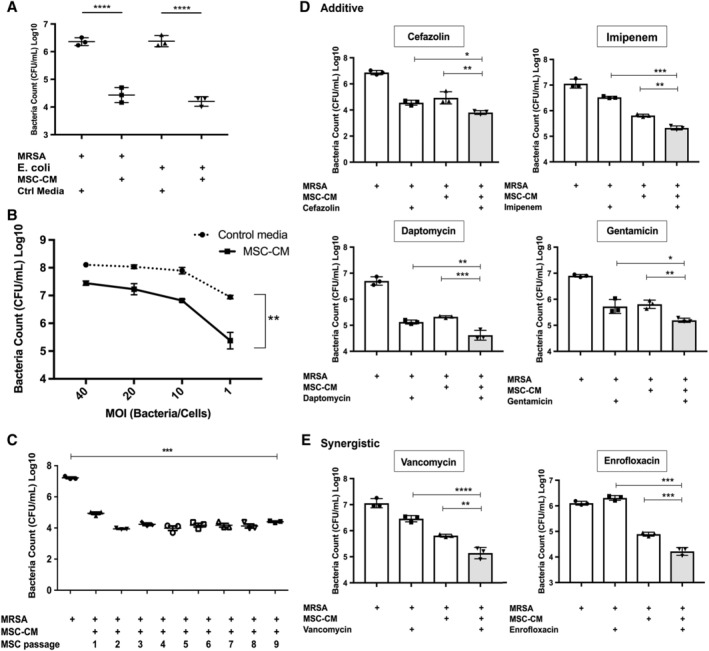
Direct antimicrobial activity of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and interaction with antibiotics in vitro. Conditioned medium (CM) from MSC was incubated with bacteria, as noted in the Materials and Methods section, to assess bactericidal activity. Data presented are representative of results obtained in three independent experiments using MSC from three different, unrelated donors. A, S. aureus and E. coli incubated with MSC CM. The y‐axis depicts bacterial colony counts (CFU/mL) in log scale. B, MSC CM incubated with increasing MOI of S. aureus. x‐axis shows depicts MOI, while dotted line represents bacterial growth when incubated with control media alone, solid line represents S. aureus CFU incubated with MSC CM. C, Bactericidal activity of MSC CM obtained from MSC at passages 1 through 9. For all figures statistical significance was determined for *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, ***P ≤ .001, ****P ≤ .0001 as assessed by one‐way ANOVA and Tukey multiple means post‐test. Error bars depicting mean with SD in all panels. D, Interaction of MSC CM with antibiotics as expressed by bactericidal activity, using the bacterial killing assay (BKA) described in the Materials and Methods section. y‐axis shows bacterial count. Antibiotics with additive effect with MSC CM for bactericidal activity are depicted, including cefazolin, imipenem, daptomycin, and gentamycin. Gray Bars represent bacterial count with the addition of MSC CM and antibiotics. E, Two antibiotics (vancomycin and enrofloxacin) in which a positive synergistic interaction with MSC CM are depicted
