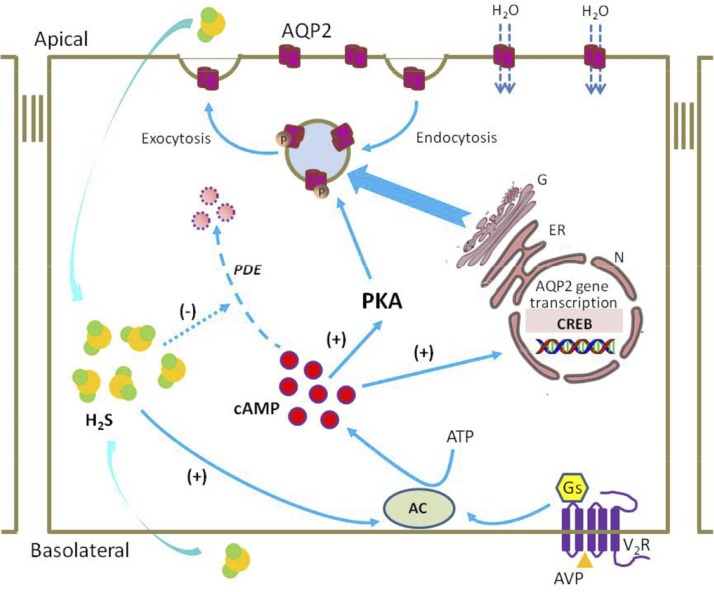
Figure 9.
A potential role for H2S in AQP-2 protein expression and trafficking in collecting duct principal cells. The H2S produced by kidney epithelial cells diffuses into principal cells and activates AC, which causes an increase in intracellular cAMP levels, activation of PKA, and subsequent phosphorylation of AQP-2. This event results in the redistribution of AQP-2 from the intracellular vesicles to the apical membrane. cAMP may also increase AQP-2 expression by activating transcription factors (e.g., CREB) that stimulate the transcription of AQP-2 at the promoter. Driven by the transcellular osmotic gradient, water enters the principal cells through AQP-2 and passes through the basolateral plasma membrane into the blood. H2S may also inhibit PDE activity, preventing the degradation of cAMP. N, nuclear; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; G, Golgi apparatus; Gs, G-protein subunit.