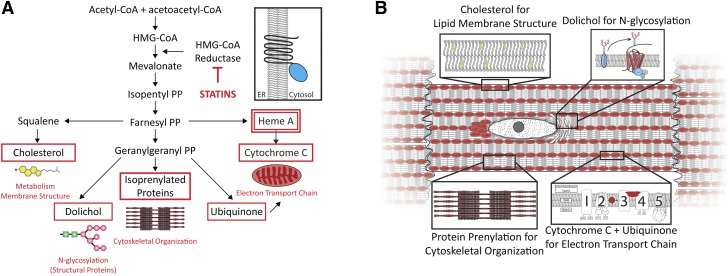
Figure 9.
Molecular pathways affected by HMG-CoA reductase inhibition: potential effects on cardiac muscle. A) HMG-CoA reductase is an ER membrane-bound protein, and multiple cellular pathways may be affected by HMG-CoA inhibition in striated muscle including: 1) cholesterol synthesis dependent lipid composition of biologic membranes (lipid rafts, caveolin); 2) dolichol synthesis and N-linked glycosylation of structural proteins (e.g., EGFR and IR-β); 3) isoprenoid synthesis and protein prenylation/farnesylation (Rap, Ras, RhoA); 4) ubiquinone production (enzyme in the electron transport system); and 5) heme A and cytochrome c synthesis. B) Ultrastructural compartments (sarcolemma, ER, mitochondria, and sarcolemma) in cardiac myocytes that may be affected by potent HMG-CoA reductase inhibition.