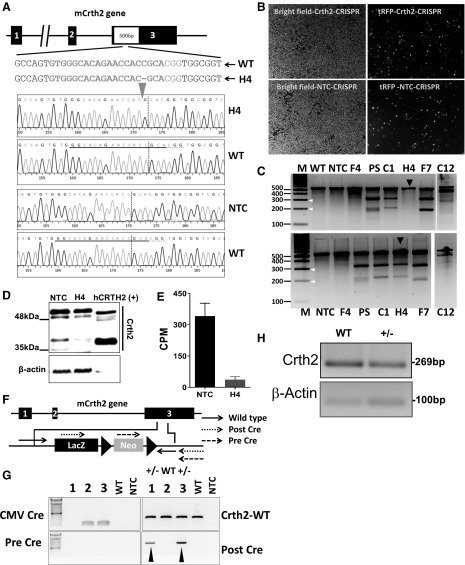
Figure 2.
Generation and validation of Crth2 KO cell line and deletion of the Crth2 gene in C57BL/6 mouse. A) Mouse Crth2 (mCrth2) gene structure composed of 3 exons and nonhomologous end joining–mediated gene editing design that targets coding region in exon 3 of the Crth2 gene, resulting in the deletion of a cytosine 4 nt upstream of the protospacer-adjacent motif sequence generating frame shift mutation. B) Representative microscopic pictures of RAW264.7 cells after 4 d of lentiviral transduction under bright field and tetramethyl rhodamine iso-thiocyabate (TRITC) filter for visualization of tRFP+ cells. C) Mismatch-specific endonuclease assay. Genomic PCR products spanning exon 3 of the Crth2 gene were amplified from WT and RAW264.7 cell mutants such as NTC, PS, F4, C1, H4, F7, and C12. White arrows indicate the size of fragments formed after the surveyor endonuclease treatment of rehybridized homoduplexes (top) or heteroduplexes (bottom). Black arrows indicate the formation of fragments upon digestion of homoduplexes (top) and heteroduplexes (bottom) of genomic PCR amplicons of H4 clone and 1:1 ratio of H4 clone and WT, respectively. NTC clones are primary sorted tRFP+ RAW264.7 cells transduced with nontargeting sgRNA and Cas9 nuclease–containing lentiviral particles. PS clones are tRFP+ RAW264.7 cells transduced with Crth2 gene–targeting sgRNA and Cas9 nuclease–containing lentiviral particles. F4, C1, H4, F7, and C12 clones are single cell clones of tRFP+ RAW264.7 cells. D) Representative immunoblot of Crth2 protein with human recombinant CRTH2 as control. E) Percent specific binding of 5 nM [3H]PGD2 in a radioligand binding assay using membranes isolated from NTC and H4 clones. Data are means ± semof technical duplicate. F) Schematic illustration of the murine Crth2 gene and design of targeting vector used for Crth2 gene deletion in ES cells to generate a Crth2 KO C57BL6 mouse colony. G) Representative genotyping PCR of WT, after-Cre, pre-Cre, and CMV-Cre BMDMs. H) Representative PCR amplicon of cDNA isolated from WT and Crth2 heterozygous BMDMs. CPM, counts per minute; CMV, cytomegalovirus; LacZ, β-galectosidase coding sequence from the E.Coli LacZ gene; Neo, coding sequences for neomycin.