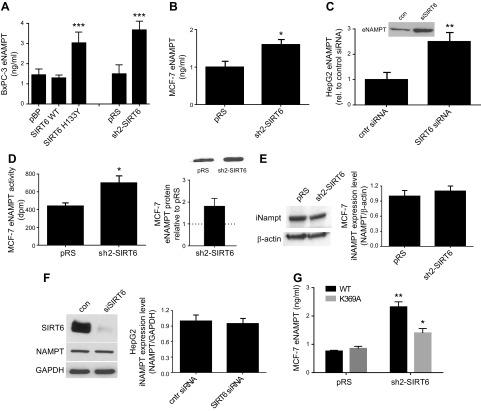
Figure 3.
Down-regulation of SIRT6 expression enhances eNAMPT secretion. A) BxPC-3 cells were engineered by retroviral transduction to express the WT form of SIRT6 (SIRT6 WT), the catalytically inactive SIRT6 mutant (SIRT6H133Y), or the empty vector pBP, or they were engineered to down-regulate SIRT6 expression (sh2-SIRT6) or the respective empty vector pRS. B, D, E) MCF-7 cells were engineered with the vector sh2-SIRT6 (to down-regulate SIRT6 expression) or with the empty vector pRS. C, F) HepG2 cells were transfected with a specific siSIRT6, or with a scramble (scr) siRNA. Cells were seeded in 6-well plates, the supernatants were collected after 48 h and eNAMPT levels were determined by an ELISA kit (A, B) or by Western blot (C, D). eNAMPT enzymatic activity in the supernatant from MCF-7 cells (D). The iNAMPT levels were evaluated by Western blot analysis in McF-7 (E) and in HepG2 lysates (F). A representative result is shown, together with the mean ± sd of 3 independent analyses. G) pRS and sh2-SIRT6 MCF-7 cells were transfected to express the WT or the K369 mutant form of NAMPT-FLAG. eNAMPT release in the supernatant was evaluated by ELISA. All results are means ± sd of results of at ≥3 independent determinations. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.