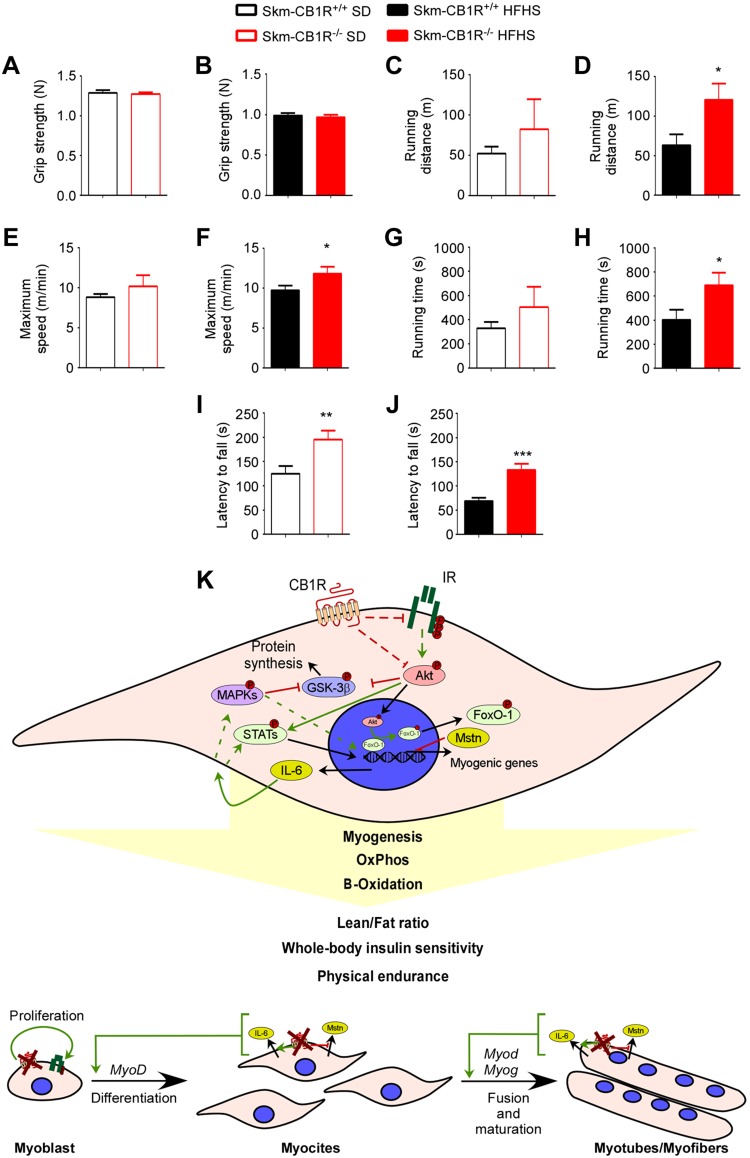
Figure 5.
Skm-CB1R−/− mice have more physical endurance than Skm-CB1R+/+ mice. A–H) Grip strength was measured in SD-fed (A) and HFHS-fed (B) Skm-CB1R+/+ and Skm-CB1R−/− mice. Maximum running distance (C, D), maximum running speed (E, F), and maximum running time (G, H) in SD-fed and HFHS-fed Skm-CB1R+/+ and Skm-CB1R−/− mice measured in a treadmill test. I, J) Mice were placed on a rotarod and time to fall in seconds was measured (n = 9 mice). Data show means ± sem. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001 (Student’s t test). K) Schema of CB1R function in skeletal muscle. CB1R down-regulates IR/AKT signaling, impacting the transcriptional regulation of the myokines Mstn and Il-6. IL-6, when secreted, activates via MAPKs signaling the myogenesis. IL-6 also impacts muscle metabolism by inducing β-oxidation and oxidative phosphorylation. Therefore, ablation of CB1R in muscle would lead to an increase in muscle mass (induce proliferation, differentiation, and fusion/maturation) and lean/fat ratio, improved whole-body insulin sensitivity, and physical endurance.