Figure 1.
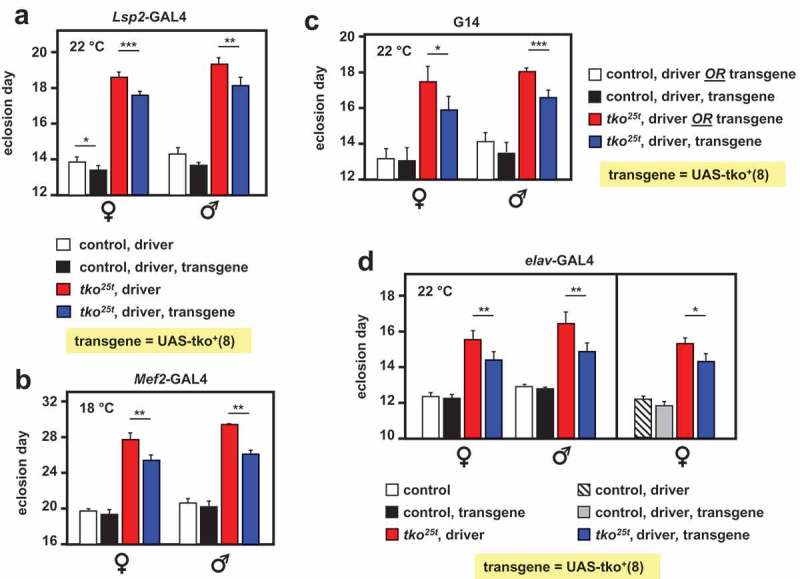
tko25t developmental delay is partially alleviated by tko+ expression directed by different drivers. Time to eclosion (means ± SD, n ≥ 3 replicate vials for each cross), of flies of the indicated genotypes, using UAS-tko+(8) with the indicated drivers. Controls were FM7 balancer flies with (a, b and d – right-hand panel) driver but no transgene, (c), driver or transgene (these classes could not be distinguished due to the nature of the cross, since the G14 driver is not viable as a homozygote), and (d – left-hand panel) neither transgene nor driver, as dictated by the chromosomal location of the drivers. Because the elav-GAL4 driver is located on the X chromosome, one of the two reciprocal crosses used in (d) generates only informative females and not males. Horizontal lines denoted by asterisks (*, **, ***) indicate significant differences in pairwise comparisons of flies of a given sex and tko genotype, with and without actively driven tko+ (Student’s t test, p < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001, respectively. The specificity of each driver was confirmed by parallel crosses in which it was used to direct the synthesis of nuclear- or membrane-localized GFP (see Fig. S1). Note that we avoided the use of the TM3 balancer because we established that it conferred a developmental delay in conjunction with tko25t, whereas the chromosome 2 balancer CyO did not (Fig. S2). The partial rescue of developmental delay was also observed at other temperatures with some drivers (see Table S1) and using the alternate transgene UAS-tko+(1) – see Figure 2. Note that most GAL4 drivers exhibit the classic pattern of temperature dependence [38], i.e. increased activity at higher temperature. However, for the strongest drivers, this may also lead to deleterious effects of over-expression at high temperature, such that a lower temperature produces optimal effects.
