Figure 6.
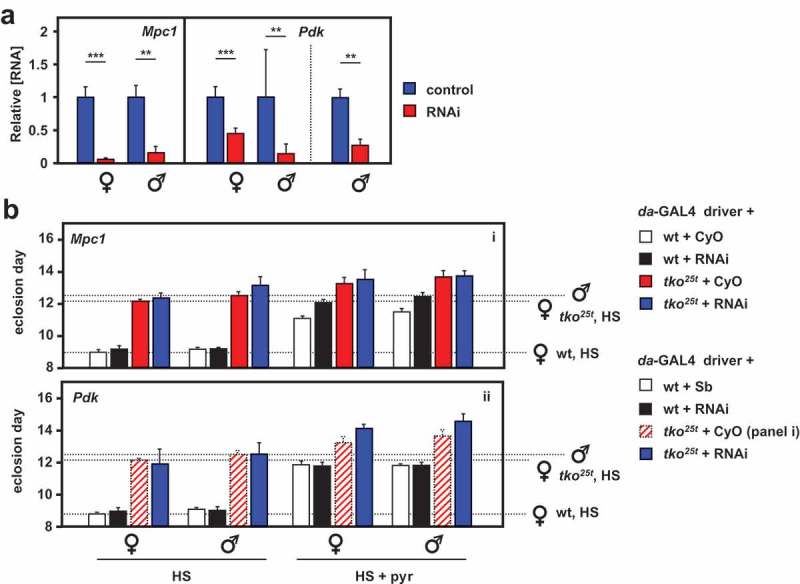
RNAi-mediated knockdown of Mpc1 or Pdk modifies the tko25t phenotype. (A) Mpc1 or Pdk RNA levels measured by qRTPCR and (B) time to eclosion of flies of the indicated genotypes (i.e. with relevant RNAi construct or balancer as shown), at 25°C, means ± SD, n ≥ 3 vials from each cross on the indicated medium: HS – high-sugar medium, with or without the addition of 25 mg/ml pyruvate. Horizontal dotted lines represent the mean eclosion times of Oregon R females and tko25t females and males on HS medium, to facilitate comparisons. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA (Fig. S6) revealed a significant effect of genotype under all conditions, but both Mpc1 and Pdk knockdown produced significant effects and showed significant interaction with genotype only in HS medium supplemented with pyruvate; Mpc1 knockdown retarding the development only of wild-type and Pdk knockdown retarding only that of tko25t flies of both sexes. Note that, in panel ii of (B), the CyO balancer flies from panel i, generated in the same experiment, are presented as the best indicative control. The TM3 balancer chromosome, whether marked with Sb or Ser, confers a developmental delay of >1 d that precludes its use as a control in such experiments, other than to allow identification of the non-balancer RNAi-bearing flies. Apart from this, all comparisons between control and knockdown flies of a given sex and genotype were from the same experiment, although Oregon R and tko25t flies were analyzed from separate crosses, as were flies cultured on different media. For a summary diagram of the reactions targeted by RNAi and by various drugs see Figure 10.
