Figure 4.
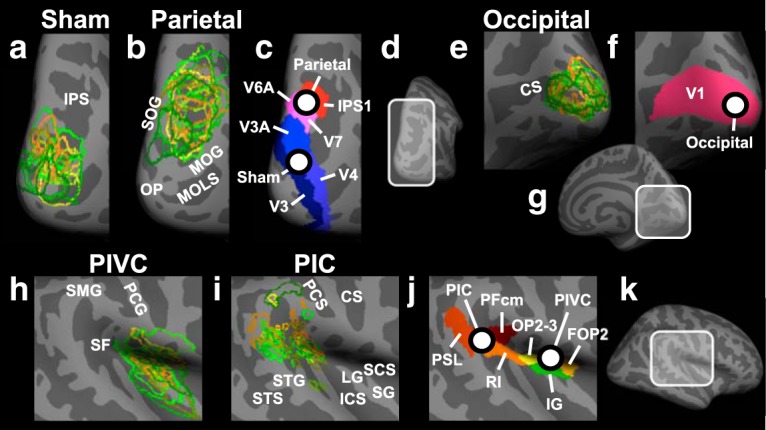
Anatomical locations of target sites for rTMS and of core areas of the vestibular cortex in the right hemisphere. a, Individual locations (for n = 15 subjects in the rTMS experiment) of the sham rTMS site (located in Brodmann area 18). Each color represents a different participant and shows the outline of the target region. The individual locations were used as target sites for rTMS. For displaying purposes, overlapping areas were remapped from the individual inflated brains to an inflated template brain. This method preserves differences in the size and location of the rTMS target sites between different subjects. The enlarged view of a subsection of the PPC is shown (see d). Light gray represents gyri. Dark gray represents sulci. IPS, Intraparietal sulcus; b, Same as in a, but for the rTMS target site in PPC. Each outline corresponds to the area of overlap between structural and functional connectivity from PIVC to PPC in a different subject. Areas of overlap were located in Brodmann areas 7 and 19. MOG, Middle occipital gyrus; MOLS, middle occipital and lunate sulcus; OP, occipital pole; SOG, superior occipital gyrus. c, Anatomical locations of the average parietal and sham rTMS sites across subjects. White dots represent the average locations of sham and parietal rTMS (referred to as “Sham” and “Parietal”; for mean Talairach coordinates, see Materials and Methods). Different colors represent different anatomical labels derived from the multimodal anatomical segmentation of the brain described by Glasser et al. (2016). IPS1, Intraparietal sulcus area 1; V3, third visual area; V3A, area V3A; V4, fourth visual area; V6A, area V6A; V7, seventh visual area. d, Subsection of PPC shown in a–c. e–g, Same as in b–d, respectively, but for the rTMS site in the OC (referred to as “Occipital”; for mean Talairach coordinates, see Materials and Methods), located in Brodmann area 17. CS, Calcarine sulcus; V1, primary visual cortex. h, Same as in a, but for PIVC. PCG, Postcentral gyrus; SF, Sylvian fissure; SMG, supramarginal gyrus. i, Same as in a, but for PIC. CS, Central sulcus; ICS, inferior circular sulcus of insula; LG, long gyrus of insula; PCS, postcentral sulcus; SCS, superior circular sulcus of insula; SG, short gyri of insula; STG, superior temporal gyrus; STS, superior temporal sulcus. j, k, Same as in c, d, but for the subsection of the Sylvian fissure and the surrounding cortex shown in h and i. FOP2, Frontal opercular area 2; IG, insular granular complex; OP2–3, parietal operculum areas 2 and 3; PFcm, area PFcm; PSL, Perisylvian language area; RI, retroinsular cortex.
