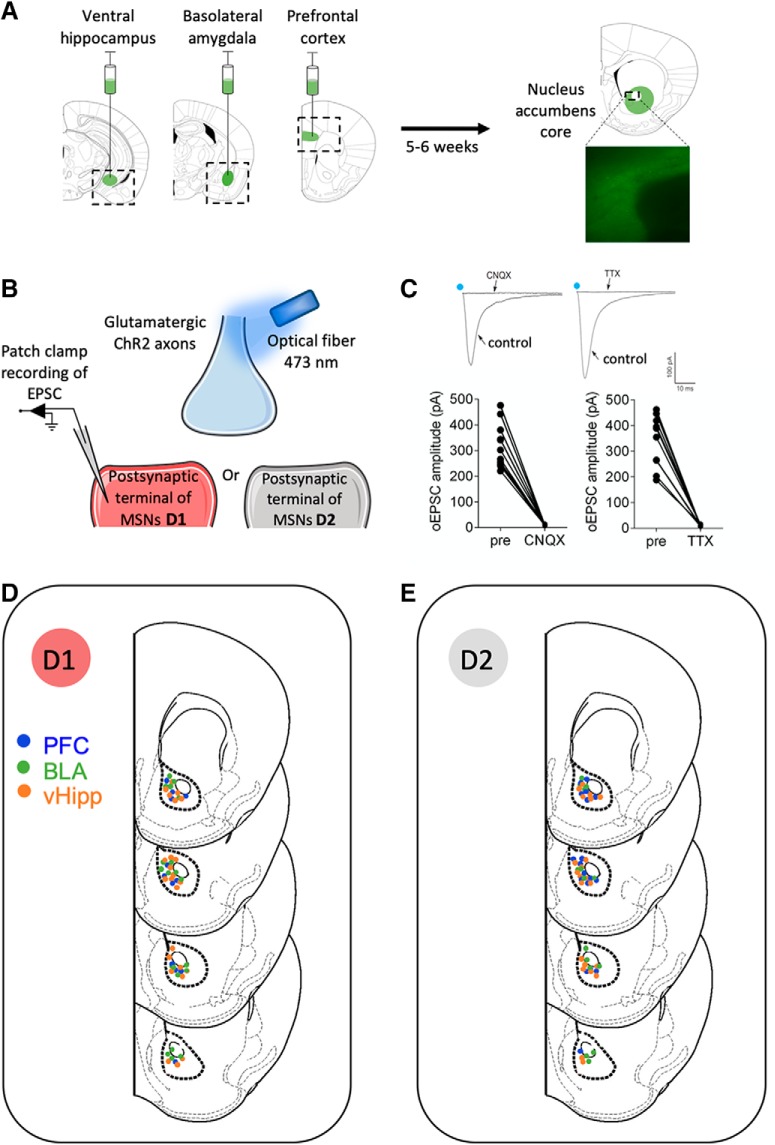
Figure 2.
Pathway-specific evoked EPSCs in the Nac core after optical stimulation of ventral hippocampal, basal amygdala or prefrontal cortex inputs. A, Representative coronal brain slices showing expression of ChR2-eYFP (green) after injections of (0.25 μl) AAV9.CaMKIIa.hChR2(H134R)-eYFP.WPRE.hGH (Addgene26969P; 1.98 × 10 GC/ml)) in the vHipp, BLA, or PFC (left). Image of ChR2-EYFP expressing axons from principal (i.e., CaMKII expressing) cortical neurons (right). B, Illustration of the experimental setup. Synaptic terminals expressing ChR2-EYFP were stimulated with a 473 nm laser coupled to an optical fiber placed 350 μm from the recording area. Recordings of optically evoked EPSCs were recorded in the whole-cell patch-clamp configuration in MSNs from the NAc core. C, Inward currents evoke by light stimulation in NAc core MSNs. CNQX (20 μm) and TTX (1 μm) completely prevented evoked currents recorded in the presence of PTX after optical stimulation of PFC inputs, showing that the oEPSCs depended on presynaptic and postsynaptic glutamate ionotropic AMPAR receptor-mediated currents. Individual oEPSCs amplitude experiments before (pre) and after CNQX (n = 10) or TTX (n = 9). Blue dots indicate optical stimulations. D, E, Location of whole-cell patch-clamped MSNs sorted by subtype in nucleus NAc core of Drd1-tdTomato transgenic mice. D1, Recordings from fluorescently labeled D1-positive MSNs (D); D2, recordings from nonfluorescently labeled MSNs (E).