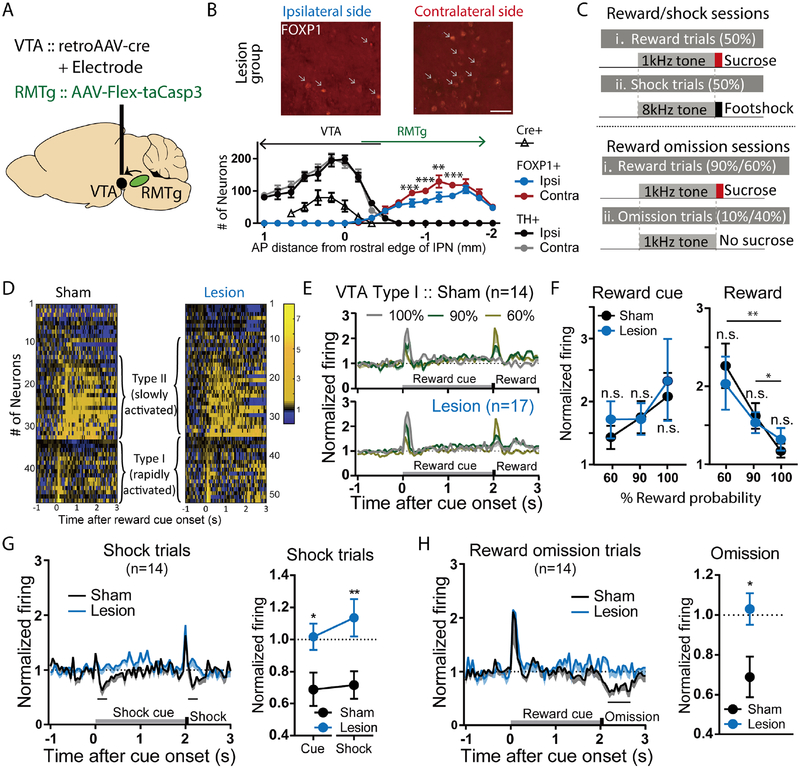
Figure 5. Selective ablation of VTA-projecting RMTg neurons abolishes VTA neuron inhibition by aversion-related signals, but not excitation to reward-related signals.
(A) Schematic of viral injections of AAV-Cre into the VTA, and AAV-FLEX-taCasp3 into the RMTg, selectively ablating VTA-projecting RMTg neurons. (B) Quantitation of RMTg FOXP1-positive cells and VTA TH-positive cells shows reduction of FOXP1 ipsilateral to AAV-Cre injection, compared with the contralateral side. Injections of FLEX-taCasp3 into RMTg were placed 1.9mm caudal to AAV-Cre injections, minimizing spread to the rostral RMTg and VTA. Scale bar: 50μm. (C) Schematic of recording sessions in which distinct auditory tones are followed by sucrose at 60%, 90%, or 100% probability, or shock at 100% probability. (D) Heatmaps of individual VTA neuron responses to reward trials. (E, F) Both sham and lesion groups show neurons that are rapidly (type I) or slowly (type II) activated by reward cues. Responses to reward cues or rewards were not affected by ablation at any of the three reward probabilities (For reward cue response, p=0.99 for 60%, 90%, and 100%, sham and lesion group; p=0.99 and p=0.92, and p=0.99 and p=0.77 for 60% vs. 90% and 60% vs. 100% in sham and lesion group, respectively. For reward response, p=0.92 for 60%, 90%, and 100% compared between sham and lesion group; p=0.01 and p=0.001, and p=0.03 and p=0.12 for 60% vs. 90% and 60% vs. 100% in sham and lesion group, respectively, two-way ANOVA, with Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test). (G, H) Type I VTA neurons were inhibited by footshocks, shock-predictive cues, and 10% reward omission. Ablation of VTA-projecting RMTg neurons eliminated all three of these inhibitions (blue traces/symbols) (shock: p=0.008, cue: p=0.044; two-way ANOVA, with Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test; 10% omission: p=0.022, paired t-test for firing rates during analysis windows shown with black bars).