Figure 1.
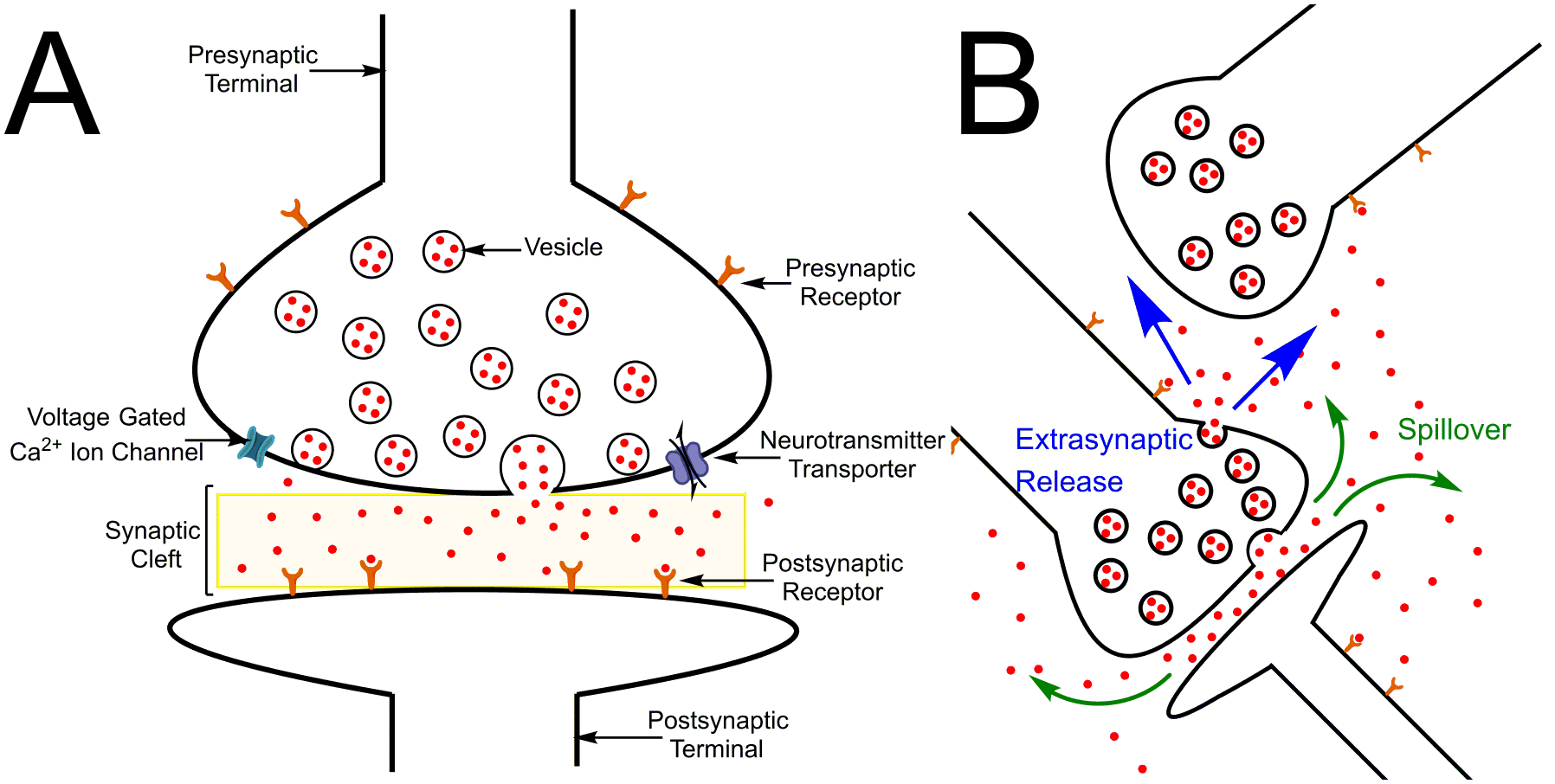
Schematics of neurotransmission. (a) Direct synaptic transmission. The neurotransmitter is released from the vesicle into the synaptic cleft and interacts with the receptor on the postsynaptic terminal. (b) Volume transmission. Two mechanisms are pictured: synaptic spillover (green) and extrasynaptic exocytosis (blue). Here, neurotransmitters diffuse and act at a more distant neuron not forming a synapse.
