FIG 1.
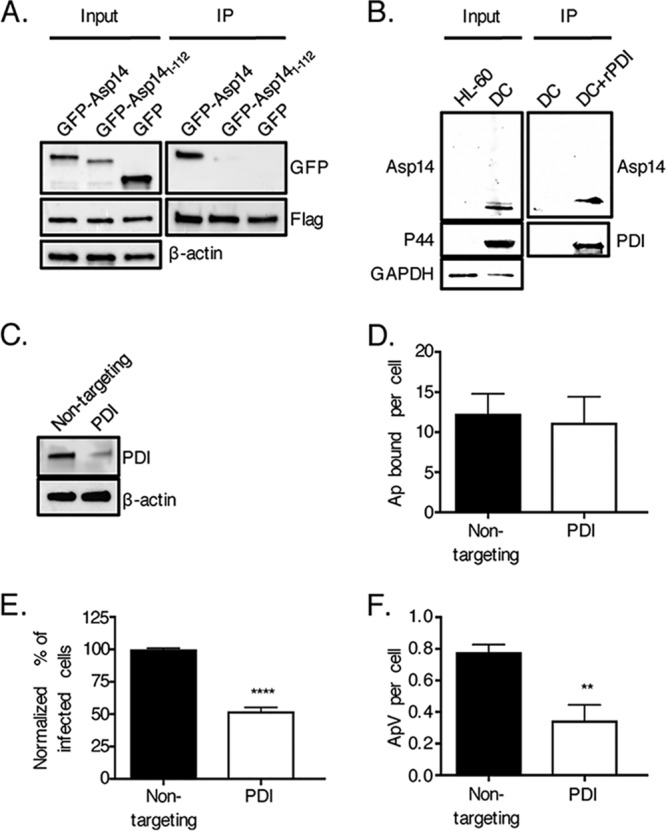
PDI is an Asp14 interacting partner and is important for A. phagocytophilum infection of host cells. (A) Asp14 is capable of binding PDI. HEK-293T cells were transfected to coexpress Flag-PDI and GFP-Asp14, GFP-Asp141–112, or GFP. Input lysates were subjected to Western blotting with GFP and Flag antibodies to verify expression of each protein of interest and with β-actin antibody to confirm that the input lysates contained equivalent amounts of protein. Whole-cell lysates were incubated with Flag antibody-conjugated agarose beads to immunoprecipitate (IP) Flag-PDI and its interacting proteins. The resulting Western blots were probed with Flag antibody to confirm that Flag-PDI was recovered and GFP antibody to determine if Flag-PDI coimmunoprecipitated GFP or either GFP-tagged protein. (B) Native Asp14 interacts with PDI. His-PDI-coupled nickel resin or nickel resin alone was incubated with A. phagocytophilum DC bacteria that had been recovered after sonication of infected HL-60 cells. After the addition of lysis buffer, His-PDI-interacting protein complexes were recovered, followed by Western blot analysis of eluted proteins and input lysates using antibodies against PDI, A. phagocytophilum P44, and human GAPDH. (C to F) PDI is important for A. phagocytophilum infection of but not binding to host cells. HEK-293T cells were treated with nontargeting or PDI-targeting siRNA. (C) PDI knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting. (D to F) Following siRNA treatment, HEK-293T cells were incubated with A. phagocytophilum organisms, followed by assessment of the numbers of bound A. phagocytophilum bacteria (Ap) per cell at 1 h (D) and the percentages of infected cells (E) and numbers of ApVs per cell (F) at 24 h. Data in panels A to C are representative of three independent experiments. Data in panels D to F are representative of three experiments conducted in triplicate. Statistically significant values are indicated. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.
