Table 3. Features of A. flavus secondary metabolite gene clusters.
| Metabolitea | Cluster numberb |
Backbone gene classification |
Cluster-specific transcriptional regulator | Number of genes in clusterc | Putative biological
function |
Representative structure |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aflatoxin | 54 | PKS | Yes | 30 | antiinsectan/oxidative stress resistance? | 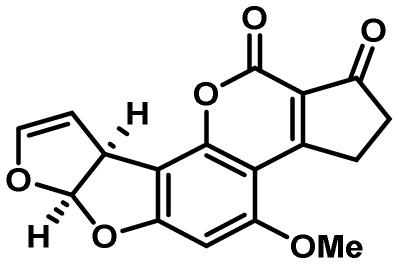 |
3,22,23 |
| Aflatrem | 15 and 32 | DMATs/GGPPs | No | 5 and 3 | antiinsectan/ antifeedant |
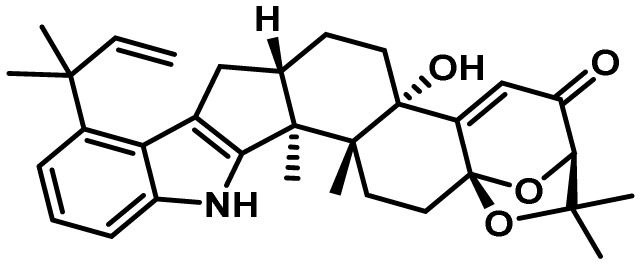 |
108,109 |
| Aflavarin | 39 | PKS | No | 5 | antiinsectan/sclerotial development | 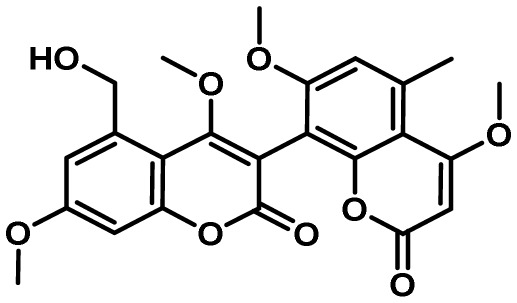 |
29 |
| Asparasone A | 27 | PKS | Yes | 4 | antiinsectan/sclerotial pigment/abiotic stress resistance | 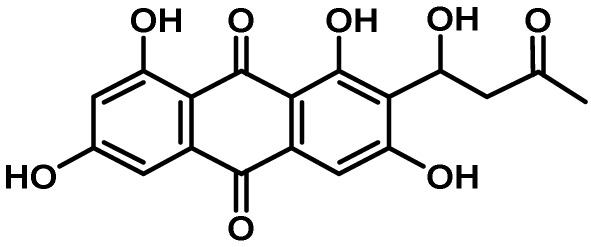 |
52 |
| Cyclopiazonic acid | 55 | DMATs/hybrid PKS-NRPS | No | 5 | mammalian antifeedant? |
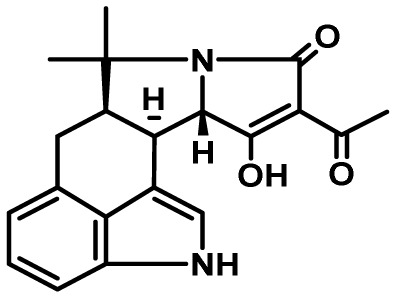 |
24,25 |
| Ditryptophenaline | 4 | NRPS | No | 3 | ? | 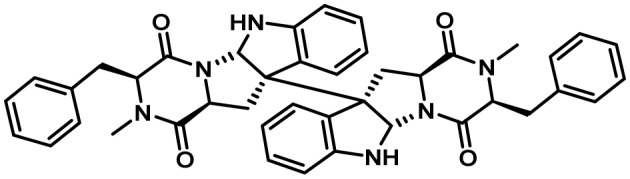 |
110 |
| Kojic acid | NA | oxidoreductase | Yes | 3 | insect
antifeedant/ antioxidant? |
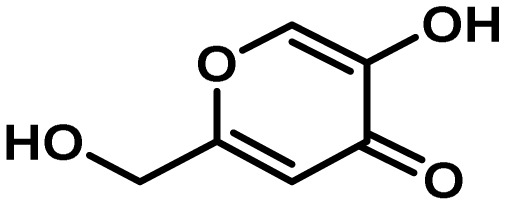 |
111 |
| Leporin | 23 | hybrid PKS-NRPS | Yes | 9 | insect antifeedant/ sclerotial development |
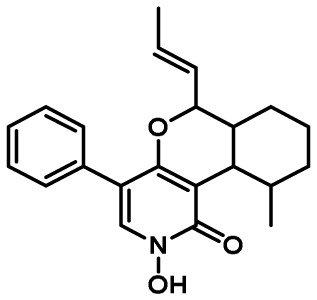 |
15 |
| Piperazine | 35 and 48 | NRPS-like | No | 6 and 6 | sclerotial development |
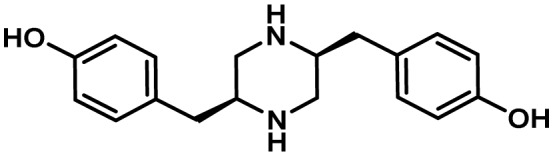 |
16 |
| Ustiloxin B | 31 | RiPPS | Yes | 15 | ? | 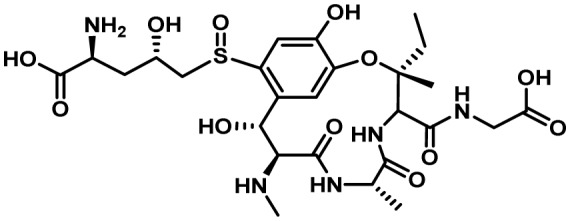 |
10,17 |
