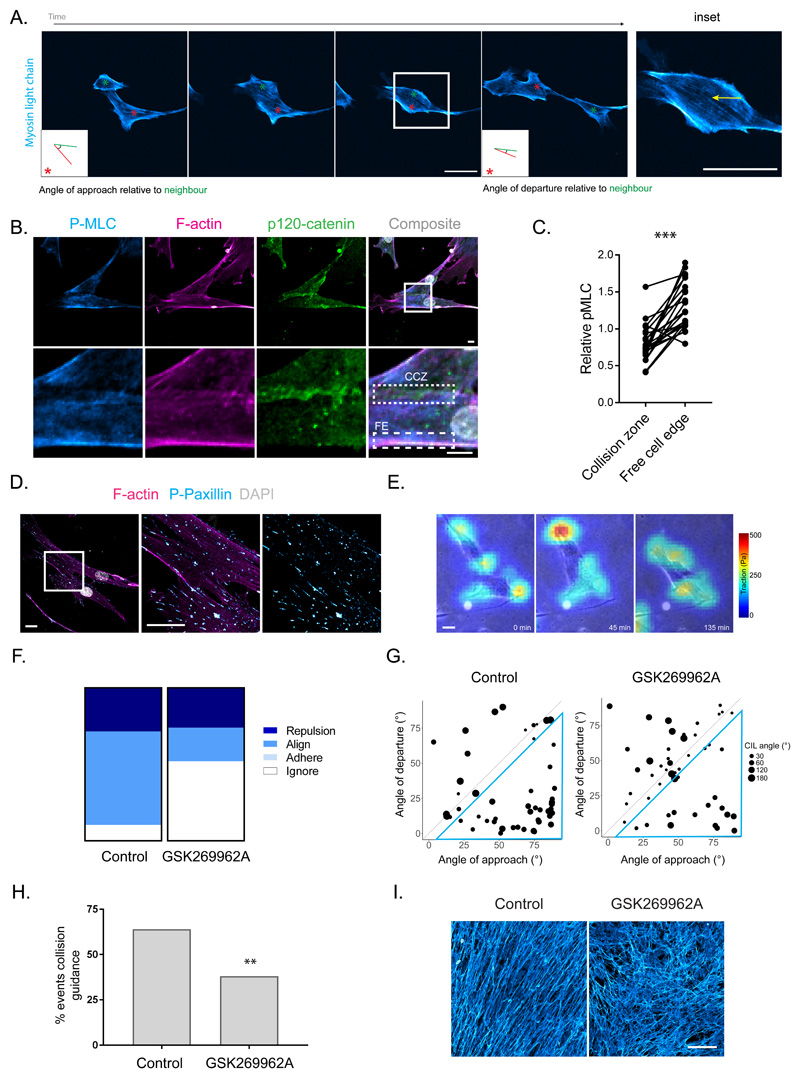
Figure 4. Collision guidance entails the suppression of actomyosin contractility at cell:cell contacts.
A. Time-lapse imaging of MLC-GFP (cyan) in aligning fibroblasts (VCAF2B) during collision guidance. Metrics for collision guidance (angle of approach and departure relative to neighbour) are shown in boxed inlay. (Representative images from three independent experiments shown). B. Immunofluorescence of pS19-MLC (cyan), p120-catenin (green) and F-actin (magenta) in aligning VCAF8 (scale bar 10μm). CCZ – Cell-cell Collision Zone, FE – Free Edge (representative images from three independent experiments shown). C. Paired measurements of pS19-MLC at cell-cell collision zones vs free edge in cells. Data are normalised to cell body pS19-MLC (n=46 in total from three independent experiments, p<0.0001 two-tailed Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test). D. Immunofluorescence of p-paxillin (cyan) and F-actin (magenta) in aligning VCAF8 (scale bar 20μm, representative images from three independent experiments shown). E. Overlaid traction force (false colour – red = high traction, cyan = low traction) and phase contrast (gray) images of VCAF8 undergoing collision guidance (scale bar 10μm, representative images from two independent experiments shown). F. Fibronectin stained FDMs from aligning (VCAF8) fibroblasts with or without ROCKi treatment (GSK269962A 20nM, scale bar 100μm, representative images from three independent experiments shown). G. Quantification of cell collisions in aligning fibroblasts (VCAF8) as either repulsion, alignment (collision guidance), adhere or ignore, with or without ROCKi treatment (n=100 collisions from two independent experiments). H. Analysis of collision guidance using the angle of approach (x axis) and departure (y axis) relative to the cell it collides with. Collisions in which angle of departure < angle of approach (inside blue triangle) reflect collision guidance events. Radius of dot indicates the CIL angle (n=100 collisions from two independent experiments). I. Quantification of collision guidance events in the presence of absence of ROCKi treatment (Collision guidance classified as collisions where angle of approach – angle of departure is between 10-90°, n=100 collisions from two independent experiments, p= 0.005, one-sided z-test).