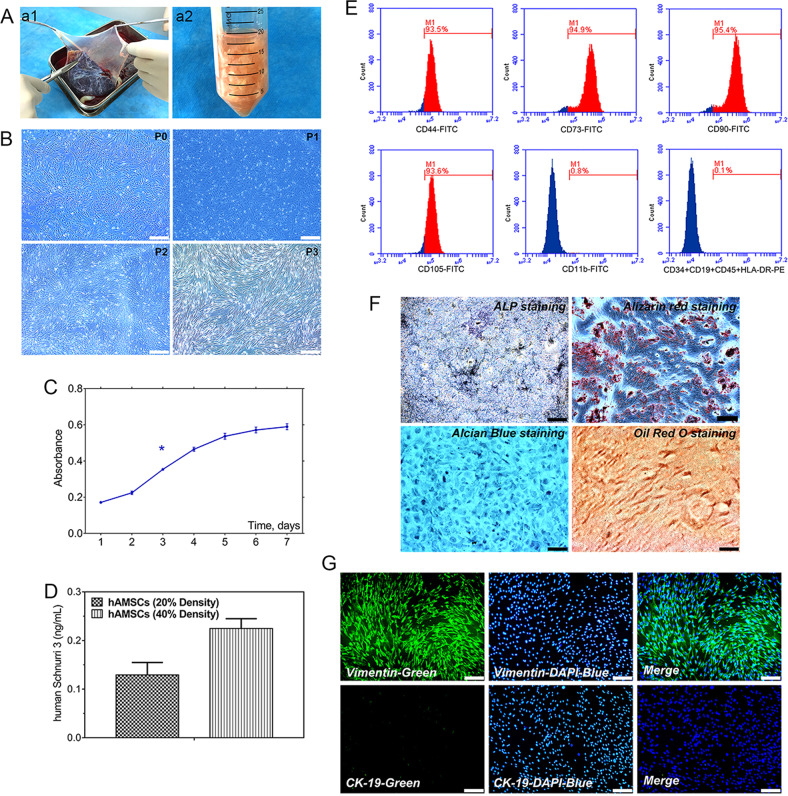
Fig. 1. Isolation and morphology of cultured hAMSCs; the proliferation potential and identification of hAMSCs; the basic expression of Shn3 in hAMSCs.
a General observation (a1), isolation, and extraction (a2) of hAMSCs. b Representative morphology of adherent hAMSCs from primary cultures (P0) were cultured through the third passage (P3) with spindle shapes on cell culture dish (original magnification ×40, scale bar = 200 μm). c Proliferation of hAMSCs as determined by the CCK-8 method showed that cells reach the doubling time at 3 days. d ELISA assay to detect the Shn3 expression in cell culture supernatants when cells reached 20% and 40% confluence, respectively. e Phenotypic properties of hAMSCs at third passage by flow cytometry and hAMSCs highly expressed CD44, CD73, CD90, and CD105 and negatively expressed CD34, CD19, CD45, and HLA-DR. f Multiple potential for osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic differentiation of hAMSCs at third passage: osteogenic (alkaline phosphatase staining and Alzarin Red S staining), chondrogenic (Alcian Blue staining), adipogenic (Oil Red O staining) (original magnification ×100, scale bar = 100 μm). g hAMSCs at third passage highly expressed vimentin and hardly expressed CK-19, and cell nuclei were stained blue by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (original magnification ×100, scale bar = 100 μm). The data are shown as mean ± SD for three separate experiments. *P < 0.05.