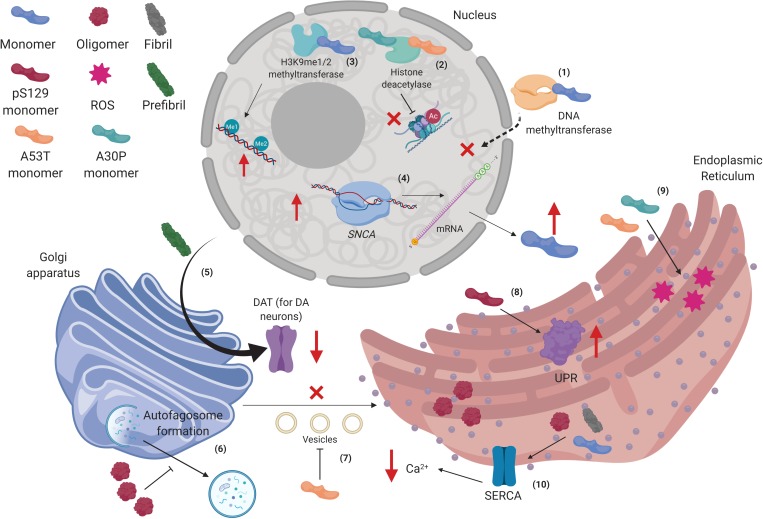
FIGURE 3.
Alpha-synuclein interactions in the nucleus, Golgi apparatus, and the endoplasmic reticulum. (1) Human wild type alpha-synuclein (hWT α-syn) can retain methyltransferases in the cytoplasm, thus altering DNA methylation of the SNCA gene. (2) hWT α-syn can also interact with H3K9me1/2 to increase mono- and dimethylation in the DNA. (3) p.A53T and p.A30P monomers bind to HDACS and inhibit histone deacetylation. (4) Decreased epigenetic regulation on the SNCA gene promotes its up-regulation, increasing α-syn transcription and further accumulation. (5) Prefibrillar α-syn can disrupt postraductional processing of dopamine transporter (DAT) in the Golgi apparatus (GA), diminishing its presence in the membrane. (6) α-syn oligomers impair autophagosome formation in the GA. (7) p.A53T monomers inhibit vesicles transport from endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to GA. (8) pS129-α-syn monomers increase unfolded protein response (UPR) activity in the ER. (9) p.A53T and p.A30P monomers increase levels of stress in the ER. (10) α-syn oligomers and fibrils affect SERCA complex in the ER, diminishing cytosolic levels of Ca2+. Created with BioRender.