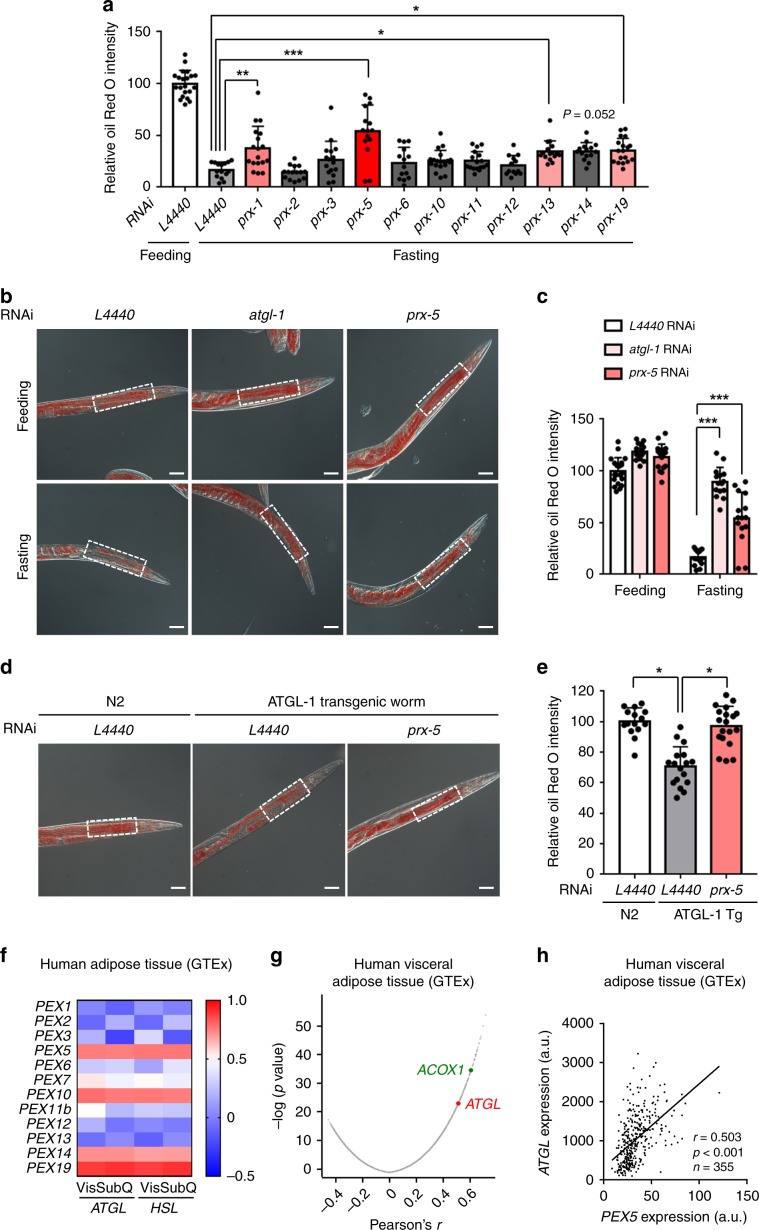
Fig. 4. PRX-5 is required for fasting-induced lipolysis in C. elegans.
a RNAi screening of peroxisomal genes involved in fasting-induced lipolysis-based Oil Red O (ORO) staining in anterior intestine of C. elegans. ORO staining intensities in young adult RNAi-treated worms under feeding and 8-h fasting conditions were quantified and classified according to the relative fold increase compared to the L4440 control group. n = 21 for feeding L4440; n = 15 for fasting L4440; n = 18 for prx-1; n = 15 for prx-2; n = 16 for prx-3; n = 15 for prx-5; n = 14 for prx-6; n = 19 for prx-10; n = 17 for prx-11; n = 13 for prx-12; n = 16 for prx-13; n = 15 for prx-14; n = 18 for prx-19. b, c Representative images and quantification of ORO staining in anterior intestine of C. elegans with RNAi of atgl-1 and prx-5 in young adult worms under feeding and fasting (8 h). n = 15–20 for quantification. n = 21 for feeding L4440; n = 16 for feeding atgl-1; n = 16 for prx-5; n = 15 for fasting L4440; n = 15 for fasting atgl-1; n = 15 for fasting prx-5. d, e Representative images and quantification of ORO staining in anterior intestine from prx-5 RNAi-treated WT worms (N2) and atgl-1 transgenic worms (ATGL-1 Tg, hj67; Is[atgl-1p::atgl-1::GFP]). n = 15 for L4440 in N2 worms; n = 17 for L4440 in ATGL-1 Tg; n = 19 for prx-5 in ATGL-1 Tg. f Heatmap analysis of Pearson’s coefficients (r) between lipolytic genes (ATGL and HSL) and PEX genes in human adipose tissue based on data from GTEx. Vis visceral; SubQ subcutaneous. g Plots of correlation between PEX5 and all detectable genes in human visceral adipose tissue based on data from GTEx. ACOX1 (green), positive control for correlation of PEX5. h Correlations between expression of PEX5 and ATGL in human visceral adipose tissue based on data from GTEx. All scale bars, 50 μm. Data represent the mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 in two-way ANOVA followed by Turkey’s post-hoc test c and unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test e.