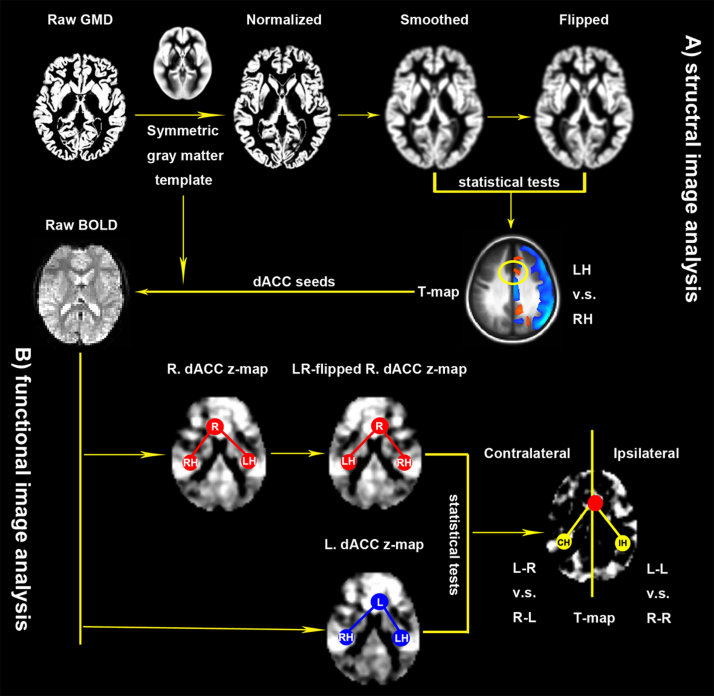
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the overall procedure of image analysis. (A) Structural image analysis. Individual raw gray matter density (GMD) images are first normalized to a symmetric gray matter template in the standard brain space and then spatially smoothed. Paired t-tests were performed on smoothed GMD images and their left–right flipped (LR-flipped) versions to achieve a T-map for GMD differences between the left hemisphere (LH) and the right hemisphere (RH). This laterality map derives seeds of regions of interests for superior and inferior subdivisions of the dorsal cingulate cortex (dACC) for next steps of functional image analysis (B). In this second stage, individual raw BOLD images are first normalized to the symmetric standard brain template and then seed-based functional connectivity maps are estimated by using the dACC seeds in both hemispheres, and quantified with their Fisher's z-maps. Flexible factor analysis is employed to detect laterality effects on both ipsilateral (L-L versus R-R) and contralateral (L-R versus R-L) functional connectivity of the dACC using the left dACC (L.dACC) seeded z-maps and the LR-flipped versions (LR-flipped R.dACC) of the right dACC (R.dACC) seeded z-maps as inputs.