Figure 7.
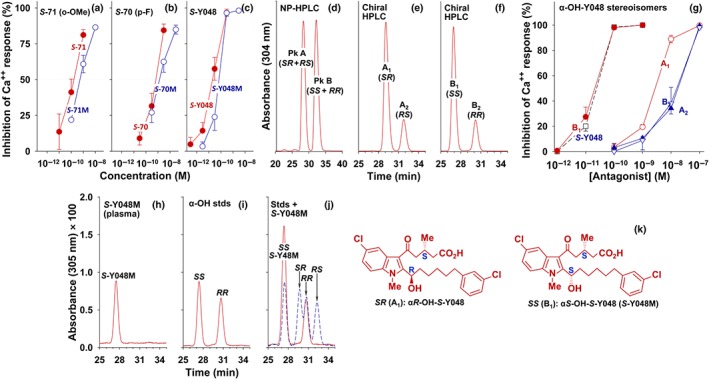
Antagonist potencies of the major plasma metabolites and their synthetic stereoisomers of some OXE receptor antagonists. The major plasma metabolites (shown as M) of (a) S‐71 (o‐methoxy‐S‐C025), (b) S‐70 (p‐fluoro‐S‐C025), and (c) S‐Y048 (m‐chloro‐S‐C025) were purified by RP‐HPLC, as shown in Figure 5, from extracts of plasma from monkeys that had received the corresponding antagonist. Metabolites purified from samples taken between 4 and 24 hr were pooled and tested for their abilities to inhibit 5‐oxo‐ETE‐induced calcium mobilization in neutrophils. The values shown for antagonists and their metabolites are means ± SEM (n = 3), except for the data shown in panel (c); n = 6. (d–f) αRS‐Hydroxy‐RS‐Y048 was prepared using the chiral synthon methyl (R)‐5‐chloro‐3‐methyl‐5‐oxopentanoate (R:S = 9:1), which in this preparation resulted in mixture of stereoisomers of α‐OH‐Y048 in which the S:R ratio for the methyl group in the acyl side chain of the final product was about 4:1. (d) Separation of RR/SS‐enantiomer pair from RS/SR‐enantiomer pair by NP‐HPLC. (e) Separation of the SR‐ and RS‐enantiomers from Peak A in panel (d) by chiral HPLC. (f) Separation of the SS‐ and RR‐enantiomers from Peak B in panel (d) by chiral HPLC. (g) Effects of synthetic S‐Y048 (□), A1 (αR‐hydroxy‐S‐Y048), A2 (αS‐hydroxy‐R‐Y048), B1 (αS‐hydroxy‐S‐Y048), and B2 (αR‐hydroxy‐R‐Y048) on 5‐oxo‐ETE‐induced calcium mobilization in human neutrophils. (h) Chiral HPLC of S‐Y048M after isolation from plasma by RP‐HPLC. (i) Chiral HPLC of a mixture of synthetic αS‐OH‐S‐Y048 and αR‐OH‐R‐Y048; (j) Co‐chromatography of S‐Y048M with the standards shown in panel (i). The dashed blue curve shows a mixture of all four synthetic stereoisomers, run separately. (k) Structures of αS‐hydroxy‐S‐Y048 (SS) and αR‐hydroxy‐S‐Y048 (SR). See Section 2 for the NP‐HPLC and chiral HPLC conditions
