Figure 2.
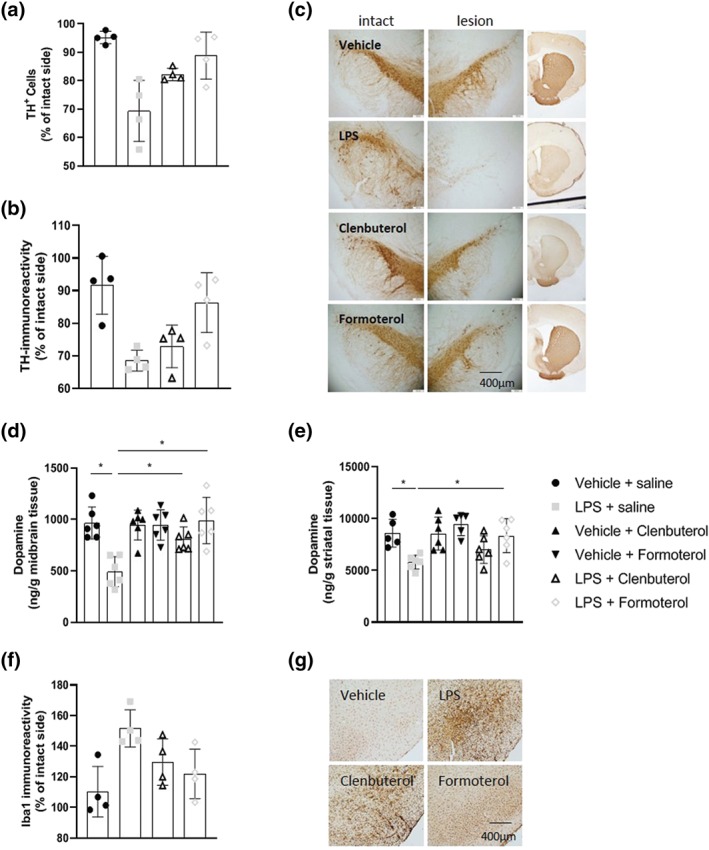
Clenbuterol and formoterol attenuate intranigral LPS‐induced loss of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons. (a) TH+ cell counts in the substantia nigra. (b) Representative images of anti‐TH immunostaining in the substantia nigra and ipsilateral striatum. (c) Area of TH immunoreactivity in the striatum. (d) Midbrain dopamine concentrations measured via HPLC. (e) Striatal dopamine concentrations measured via HPLC. The effect of clenbuterol and formoterol treatment was assessed on nigrostriatal dopamine neurons and midbrain and striatal dopamine concentrations 2 weeks 14 days following intranigral LPS administration. Treatment with clenbuterol (100 μg·kg−1 i.p.) or formoterol (100 μg·kg−1 i.p.) began 4 hr following LPS and continued for 7 days (q.d.). Intranigral LPS induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration along the nigrostriatal tract. Treatment with clenbuterol and formoterol attenuated the loss of dopamine neurons and suppressed reductions in nigrostriatal dopamine content. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 for immunoreactivity; n = 6 for dopamine concentrations), * P < .05 via one‐way ANOVA with post 14 days following intranigral LPS administration. hoc Newman–Keuls
