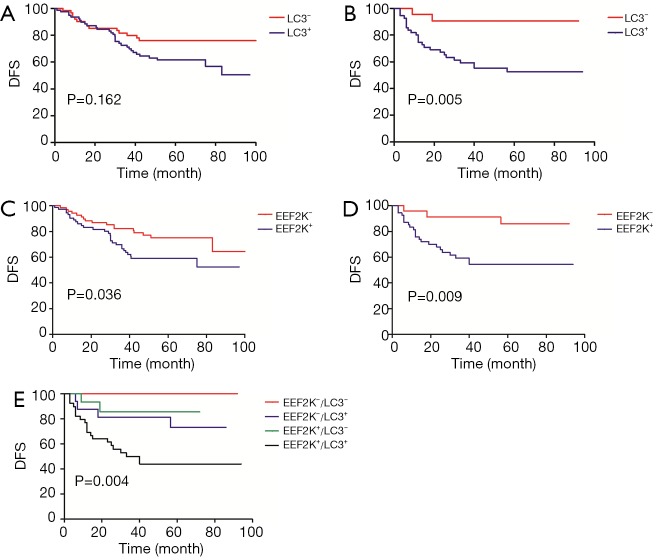
Figure 4.
DFS according to LC3 and eEF2K status for different breast cancer subtypes. (A) DFS according to LC3 in luminal-like tumors (P=0.162); (B) DFS according to LC3 in TNBC tumors; LC3 positivity was correlated with poor survival (P=0.005); (C) DFS according to eEF2K in luminal-like tumors; eEF2K positivity was correlated with poor survival (P=0.036); (D) DFS according to eEF2K in TNBC tumors; eEF2K positivity was correlated with poor survival (P=0.009); (E) DFS according to the risk groups classified by LC3 and eEF2K. All TNBC patients were classified into the following four subgroups: eEF2K−/LC3− (n=8); eEF2K−/LC3+ (n=16); eEF2K+/LC3− (n=15); and eEF2K+/LC3+ (n=39) (P=0.004). DFS, disease-free survival; eEF2K, eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase; TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer.