Fig. 1.
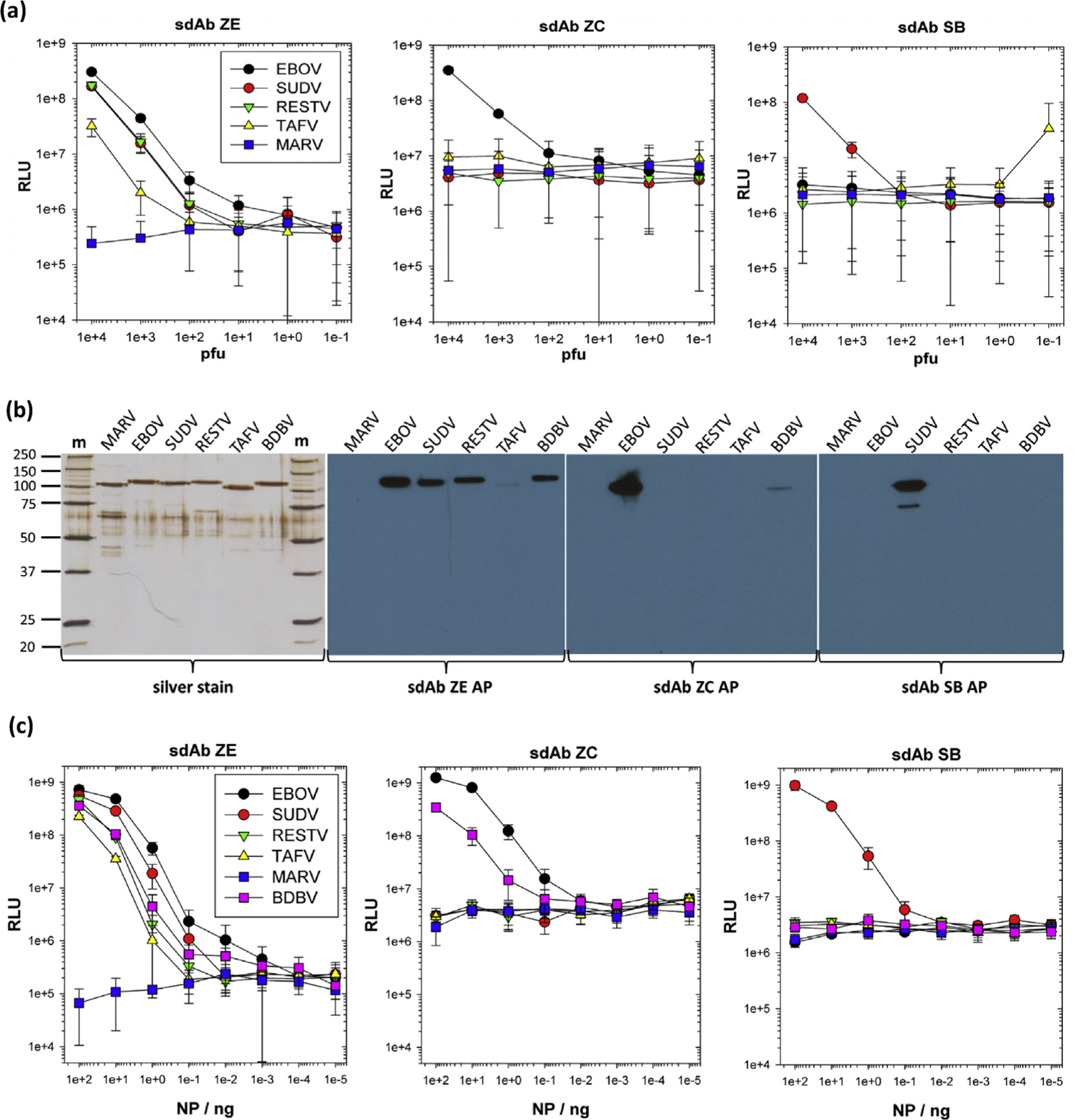
Transitioning from live virus to recombinant NP for reassessment of sdAb specificities. (a) Monoclonal affinity reagent sandwich assay (MARSA) using each of the sdAb as neutravidin oriented captor and phage displayed tracer to reconfirm cross-reactivity profiles on EBOV, SUDV, RESTV, and TAFV and the negative control MARV. The legend is within the sdAb ZE graph and is the same for all panels. The experiment was repeated on two different occasions, and the error bars represent ±SD. (b) Analysis of 250 ng of purified recombinant NP from HEK293T lysates after density gradient centrifugation by SDS-PAGE and silver staining plus Western blotting and probing with 100 nM alkaline phosphatase (AP) fusions of sdAb ZE, ZC, or SB. (c) Titration of recombinant NP within the MARSA using the oriented sdAb captor and phage tracer. The legend is within the sdAb ZE graph and is the same for all panels. The experiment was repeated on two different occasions and the error bars represent ±SD. BDBV, Bundibugyo ebolavirus; EBOV, Zaire ebolavirus; m, molecular weight marker with sizes in kDa; MARV, Marburg virus; NP, nucleoprotein; RESTV, Reston ebolavirus; RLU, relative light units; SD, standard deviation; SUDV, Sudan ebolavirus; TAFV, Taï Forest ebolavirus;sdAb, single-domain antibody.
