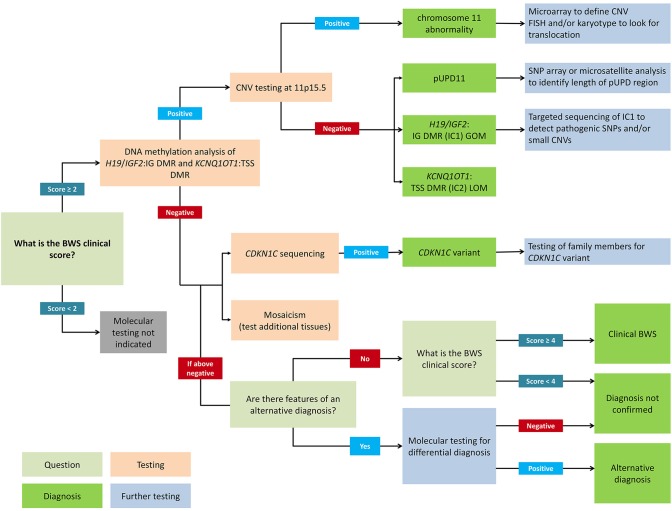
Figure 2.
Flowchart for molecular diagnosis of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Patients with BWS clinical score ≥2 should receive genetic testing while patients with clinical score <2 do not meet the criteria for testing. Recommended first-line testing (highlighted in orange) should analyze methylation at H19/IGF2:IG DMR (IC1) and KCNQ1OT1:TSS DMR (IC2) and copy number variation (CNV). These tests can yield positive molecular diagnoses of chromosome 11 abnormalities, paternal uniparental disomy of chromosome 11 (pUPD), IC1 gain of methylation (IC1 GOM), and IC2 loss of methylation (IC2 LOM) (highlighted in dark green). Further testing (highlighted in blue) can determine chromosomal abnormalities more precisely. If DNA methylation testing is negative, CDKN1C sequencing is recommended, or additional tests for rare chromosomal translocations. Negative test results can also be due to tissue mosaicism, and additional tissue samples can be tested. Differential diagnoses should also be considered, but patients with clinical score ≥4 can have a clinical diagnosis of BWS even without molecular confirmation. Adapted from Brioude et al. (2).