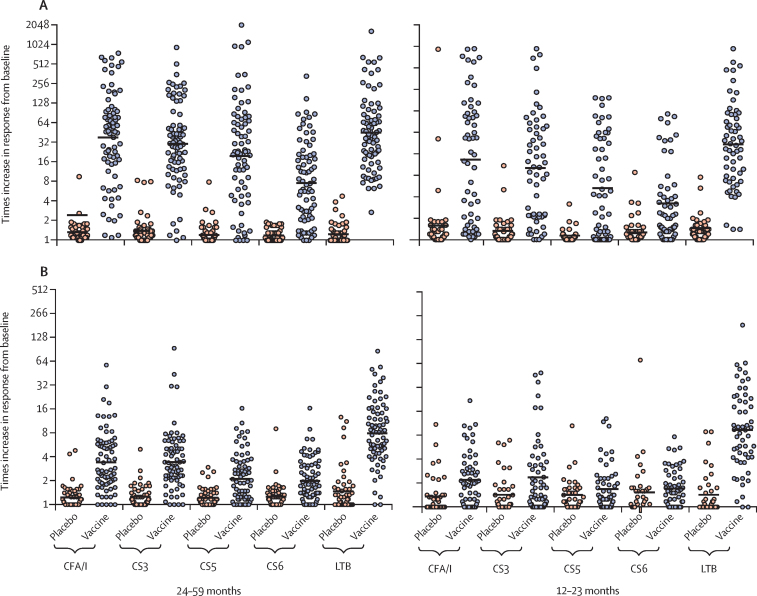
Figure 1.
Geometric mean times increases in ALS (A) and plasma (B) IgA responses in children aged 12–59 months
Horizontal lines indicate the geometric mean response for the group, whereas the circles represent individual responses. Times increases were calculated as the post-immunisation response (the highest response on either day 7 after the first dose or day 5 after the second dose) divided by pre-immunisation antibody level. Geometric mean times increases in ALS concentrations were significantly different between vaccine and placebo recipients for all antigens in both age groups (all p<0·0001 with Student's t test and all p<0·0005 with Holm's-Bonferroni adjustment). In children aged 24–59 months, geometric mean times increases in plasma IgA concentrations were significantly different between vaccine (n=75) and placebo (n=50) recipients for all antigens (all p<0·0001 with Student's t test and all p=0·0005 with Holm's-Bonferroni adjustment); in children aged 12–23 months, the difference between vaccine (n=60) and placebo (n=40) recipients was significant only for CFA/I, CS3, and LTB (all p≤0·0061 with Student's t test and all p≤0·018 with Holm's-Bonferroni adjustment). ALS=antibodies in lymphocyte secretions.