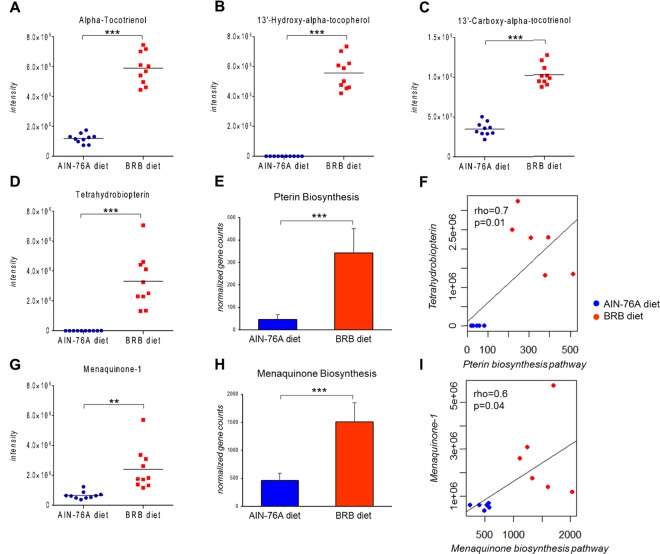
Figure 3.
BRB consumption significantly increased vitamin-related metabolites in the mouse gut microbiome, as exemplified by vitamin E metabolites (A–C), cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (D) and menaquinone-1 (G); meanwhile, gut bacterial pathways involved in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin (E) and menaquinone (H) were upregulated in mice fed BRB, which shows clear correlation with the abundance of corresponding metabolites (F, I) (p < 0.05; ρ > 0.5). (***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05).