Fig. 3.
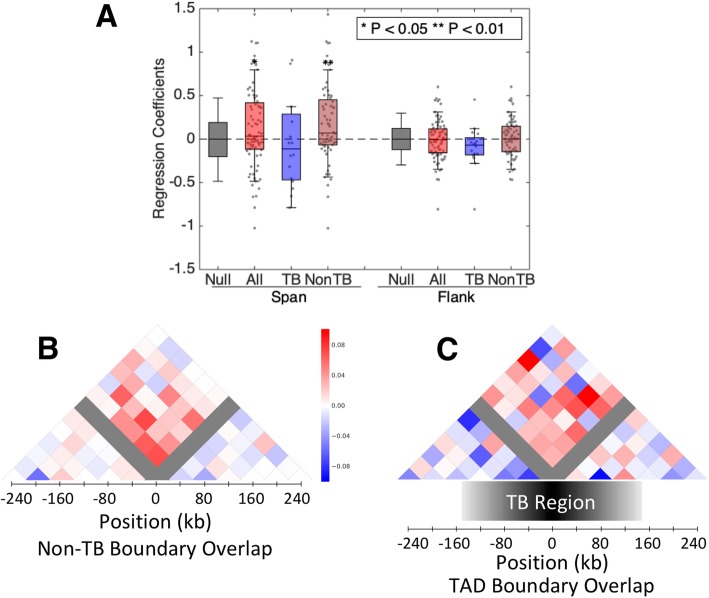
Large deletions that do not intersect a TAD boundary have a significant positive effect on the number of contacts that span the deletion region. To determine if the strength or direction of effects differed for deletions located at the boundaries of TADs, regression coefficients from our genome wide analysis were compared between groups of deletions located at TAD boundaries (TB) and those not at TAD boundaries (NonTB) (Panel a). A Wilcoxon rank-sum test was performed for each group against a null distribution, resulting in a significant positive effect for the span region of NonTB deletions (p-value: 0.002). To visualize the topological changes of these effects, a blue-red heatmap of regression coefficients was constructed for NonTB and TB deletions separately. A linear regression was performed for each pairwise bin interaction and coefficients were averaged across deletions. Deletions not present at TAD boundaries have positive values in the span region (Panel b). Deletions that intersect TAD boundaries do not have a unique trend in the span or flank region (Panel c)