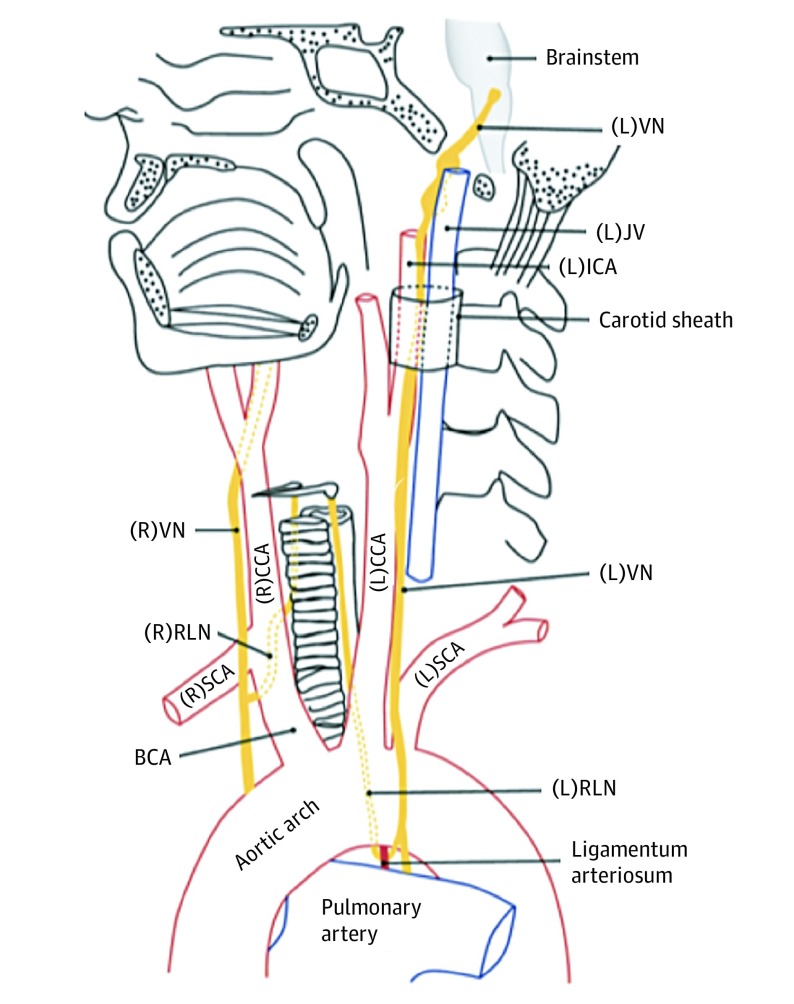
Figure 1. Normal Anatomy of the Vagus Nerves (VNs) and Recurrent Laryngeal Nerves (RLNs).
The left VN exits the skull base through the jugular foramen and descends through the neck posterolateral to the internal carotid arteries (ICAs) and common carotid arteries (CCAs). As the left VN passes anterolateral to the aortic arch, the left RLN branches off and passes below the arch posterior to the ligamentum arteriosum. It then ascends within the left tracheoesophageal groove to enter the larynx posteriorly at the level of the cricoarytenoid joint. The right VN descends posterolateral to the right ICA and CCA from the right jugular foramen, giving rise to the right RLN as it passes anterior to the right subclavian artery (SCA). The right RLN then passes posterior to the right brachiocephalic artery (BCA) before ascending to the larynx within the right tracheoesophageal groove. Adapted with permission from the Radiological Society of North America. JV indicates jugular vein; L, left; and R, right.