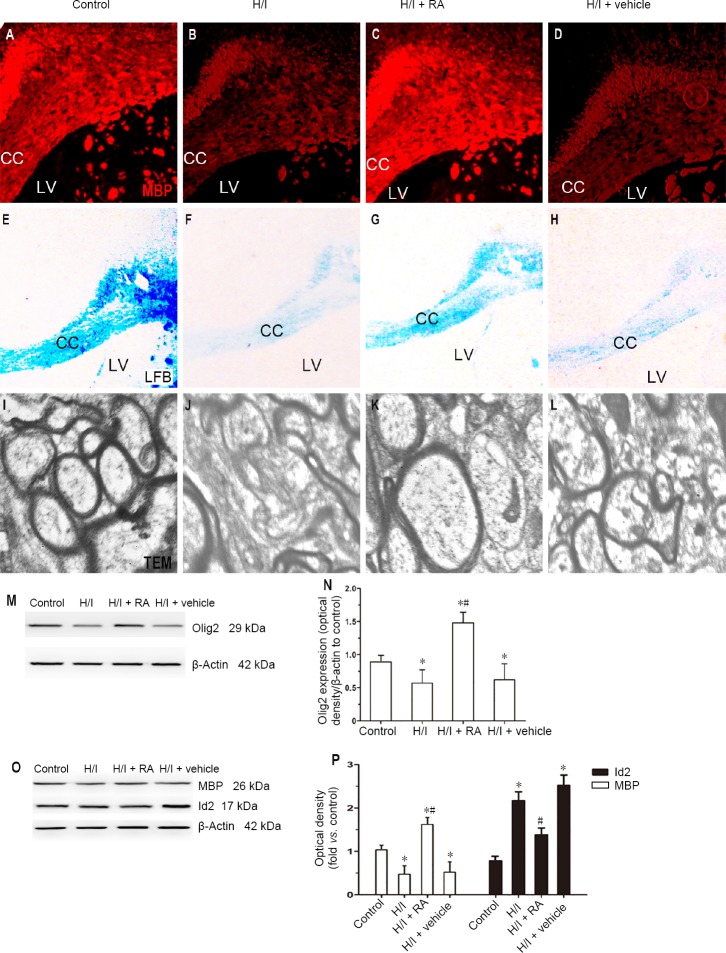
Figure 4.
Effect of RA on the expression of myelin-associated protein and myelin morphology in H/I injured rats at 50 days after birth.
(A–D) Immunopositivity of MBP in the CC was stained among four groups. (E–H) LFB was used to detect the status of myelination in the CC. (I–L) TEM was used to observe the morphological changes of myelin sheaths in the CC. H/I injury down-regulated the expression of MBP in the CC. The myelinated nerve fibers of the control group were stained blue in the CC, whereas blue staining was rarely observed in the CC of H/I injured rats. In contrast, H/I damage resulted in a decrease in the bulk density of myelinated axons in the CC and a decrease in axonal diameter. RA treatment significantly reduced the effects of H/I injury, partially improving the packing density of the myelinated axons and improving their diameters. (M, N) Western blot assay of the Olig2 expression in the CC. (O, P) Quantification of western blot assays of the MBP and Id2 expression in the CC. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05, vs. control group; #P < 0.05, vs. H/I group (one-way analysis of variance followed by post hoc Tukey’s tests). CC: Corpus callosum; H/I: hypoxia/ischemia; Id2: DNA binding 2; LFB: luxol fast blue staining: LV: lateral ventricle; MBP: myelin basic protein; RA: rosmarinic acid; TEM: transmission electron microscopy.