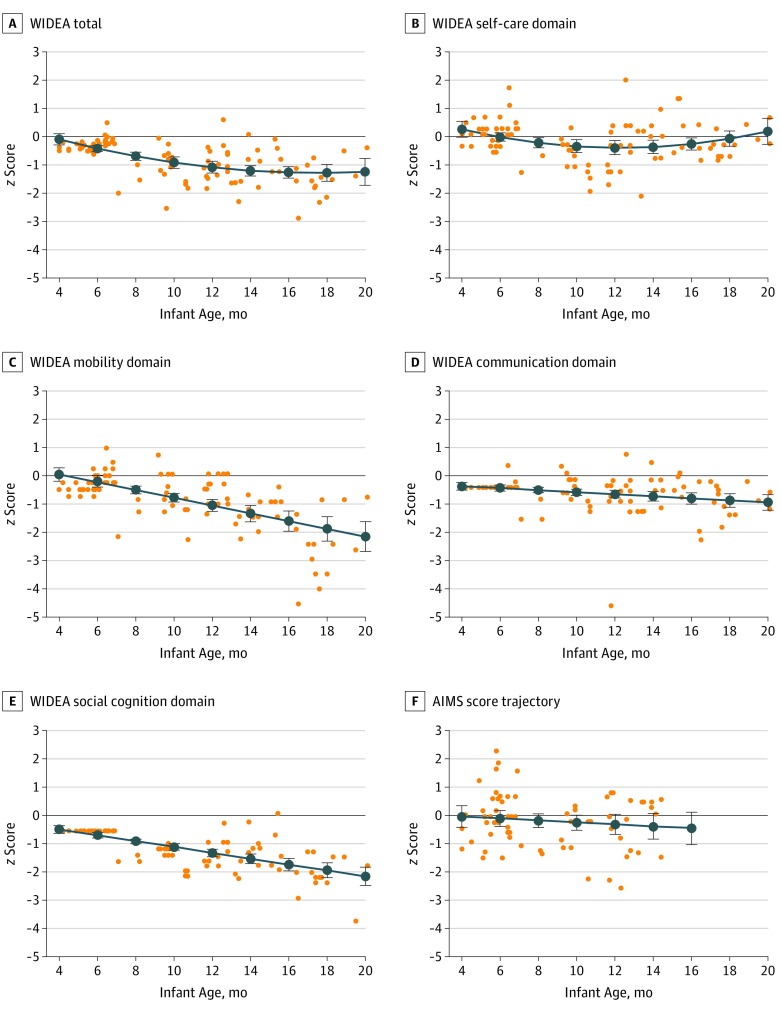
Figure 1. Infant Warner Initial Developmental Evaluation of Adaptive and Functional Skills (WIDEA) and Alberta Infant Motor Scale (AIMS) z Scores Over Time .
The WIDEA total, WIDEA domains, and AIMS z score trajectories were modeled over time in 70 infants with in utero Zika virus (ZIKV) exposure. z Scores at each assessment are shown as orange dots, and the modeled trajectory is shown as a blue line with 95% CI bars. The infants exposed to ZIKV in utero showed evidence of decline in WIDEA total z scores (A; coefficients: age = –0.227 vs age2 = 0.006; P < .003) and in the domains of self-care (B; coefficients: age = –0.238 vs age2 = 0.01; P < .008), mobility (C; –0.14; P < .001), communication (D; –0.036; P = .001), and social cognition (E; –0.10; P < .001). AIMS z scores (F) showed evidence consistent with modest decline, although not statistically significant, by infant age in months (excluding infants >15 months of age) (95% CI, –0.107 to 0.037; P = .34).