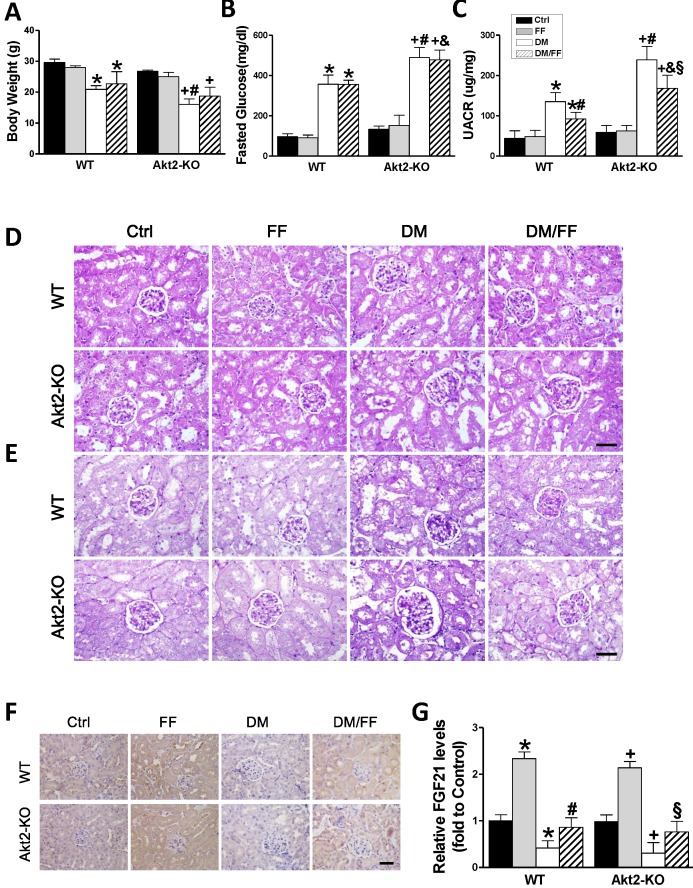
Figure 5.
Effects of FF on Akt2-KO and WT mice with diabetes. Diabetes was induced by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 150 mg/kg), and then mice were administered FF (100 mg/kg) or vehicle by gavage every other day for 3 months. Body mass (A), fasting glucose (B), and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR, C) were measured or calculated at the end of the treatment period. Renal histology (D) and glycogen deposition (purple) (E) were assessed following hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining of kidney sections (400 ×, scale bar 100 μm), respectively. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) for fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) (F; brown: positive staining) was performed in kidney sections (400 ×, scale bar 100 μm), followed by quantitative analysis (G). Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n≥5). *, p < 0.05 vs. the corresponding WT/Ctrl; #, p < 0.05 vs. the corresponding WT/DM; &, p < 0.05 vs. the corresponding WT/DM/FF; +, p < 0.05 vs. the corresponding Akt2-KO/Ctrl; §, p < 0.05 vs. the corresponding Akt2-KO/DM.