Figure 5.
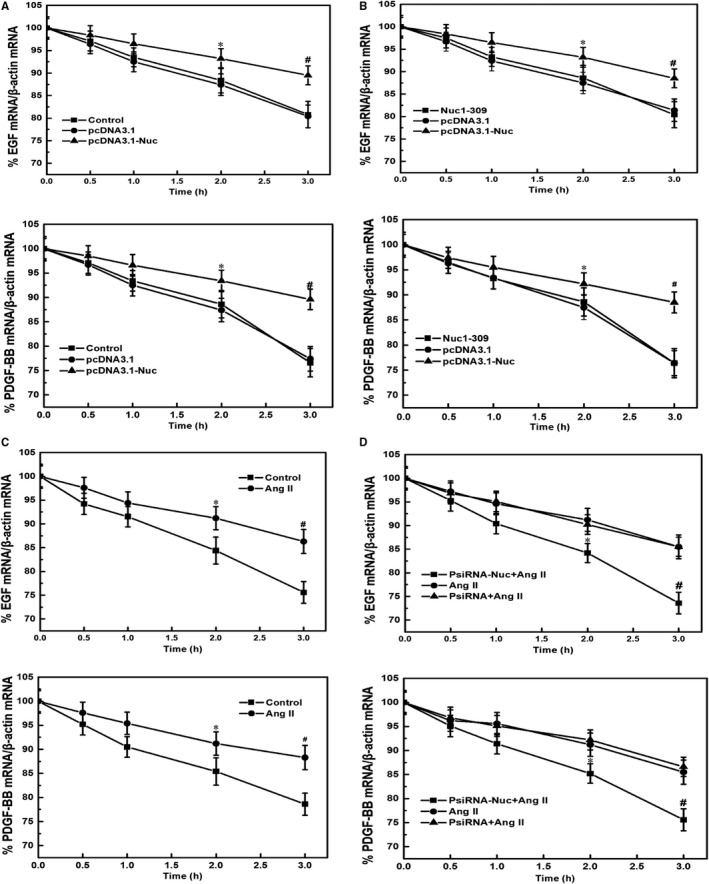
The effect of nucleolin overexpression and low expression on the stability of EGF and PDGF‐BB mRNA. A, Effect of nucleolin overexpression on the stability of EGF and PDGF. B, Effect of nucleolin mutant (Nuc1‐309) on the stability of EGF and PDGF. VSMCs were transiently transfected with nucleolin overexpression plasmid and its mutant expression plasmid for 48 h. After adding the transcription inhibitor actinomycin D (actinomycin D, 5 μg/mL), the cells were collected at different time‐points (0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 h), and the mRNA levels of EGF and PDGF were detected by RT‐qPCR. Control: normal VSMCs; pcDNA3.1: control plasmid group; pcDNA3.1‐Nuc: nucleolin overexpression plasmid group; Nuc1‐309: nucleolin mutant plasmid lacking the carboxy terminus of nucleolin (ie deleting the amino acid containing the RNA‐binding domain); β‐actin was used an internal control (Data were expressed as X ± S, n = 5; * P < .05, # P < .01 vs the pcDNA3.1 and Nuc1‐309 group.) (C) Effect of Ang II on the stability of EGF and PDGF. After treatment of VSMCs with 10−5 mmol/L Ang II for 48 h, cells were harvested at different time‐points (0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 h) after adding the transcription inhibitor actinomycin D (5 μg/mL), and the mRNA levels of EGF and PDGF were detected by RT‐qPCR. Control: normal VSMC group; Ang II: Ang II treatment group; β‐actin was internal control (Data were expressed as X ± S, n = 5; * P < .05, # P < .01 vs the control group). D, Effect of low expression of nucleolin on the stability of EGF and PDGF induced by Ang II. After VSMCs were transfected with nucleolin interference plasmid for 24 h, VSMCs were treated with 10−5 mmol/L Ang II for 48 h, cells were harvested at different time‐points (0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 h) after adding the transcription inhibitor actinomycin D (5 μg/mL), and the mRNA levels of EGF and PDGF were detected by RT‐qPCR. Ang II: Ang II treatment group; PsiRNA: control plasmid; PsiRNA‐Nuc: nucleolin RNA interference plasmid. β‐actin was used as an internal control (Data were expressed as X ± S, n = 5; * P < .05, # P < .01 vs the PsiRNA and Ang II‐treated group)
