Figure 3.
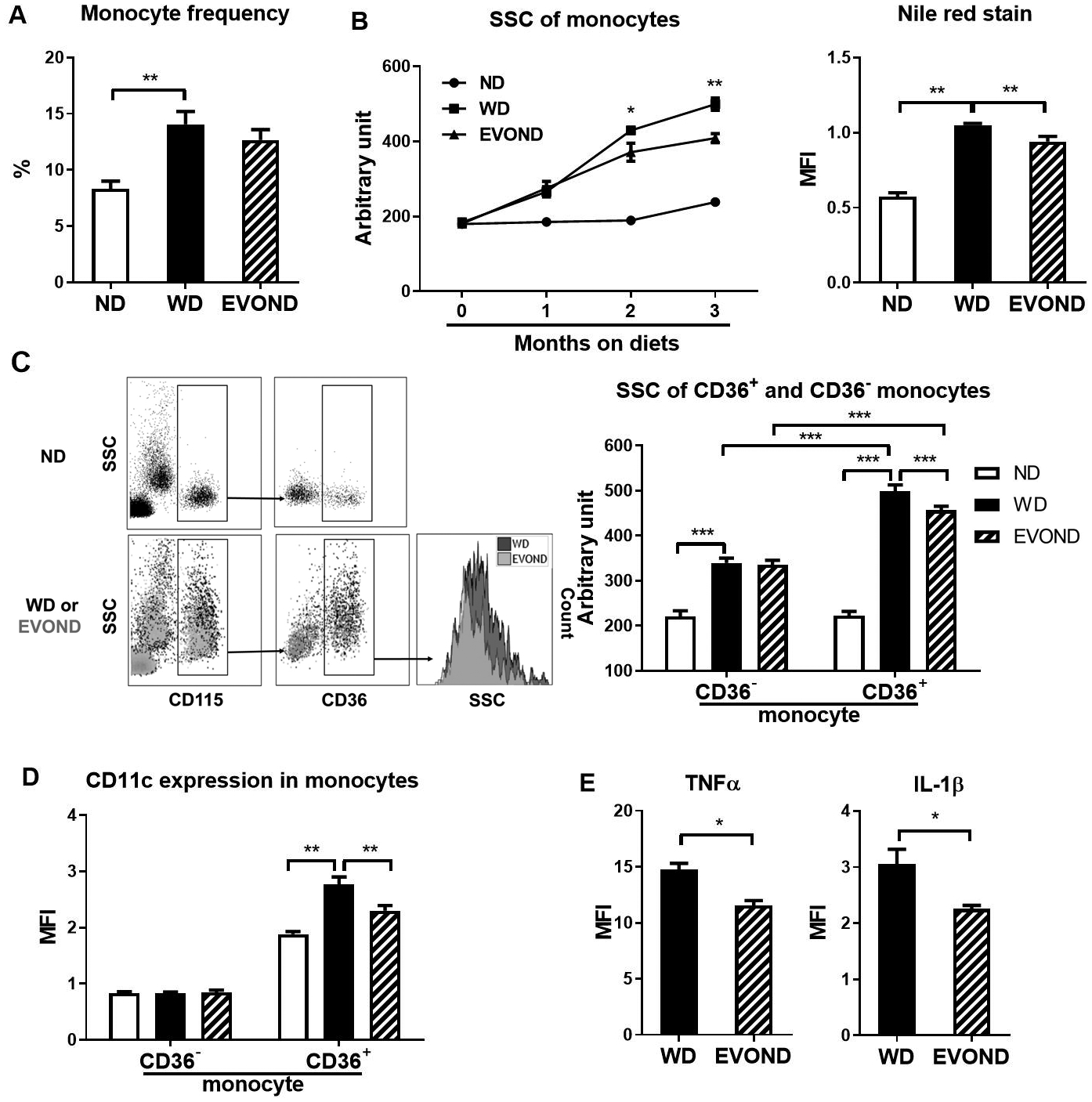
EVOND compared to WD reduced foamy monocyte formation and inflammation in Ldlr–/– mice. A, Monocyte frequency in total leukocytes of mice on ND, WD, and EVOND (n=12–20/group). B, Side scatter (SSC) value and Nile red mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of circulating monocytes of mice on different diets (3 months on diets for Nile red staining). C, Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) examples showing foamy monocytes in blood of Ldlr–/– mice on different diets (left panel). Monocytes (CD115+) were divided into two subsets based on CD36. Elevations in SSC indicated lipid accumulation and foamy monocyte formation; quantification of SSC values of CD36– and CD36+ monocytes in Ldlr–/– mice on diets (n=9–18/group; right panel). D, CD11c expression on CD36– and CD36+ monocytes in Ldlr–/– mice on diets (n=9–18/group). E, Expression of TNFα and IL-1β in monocytes of Ldlr–/– mice on diets (n=4/group). Data are shown as mean±SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
