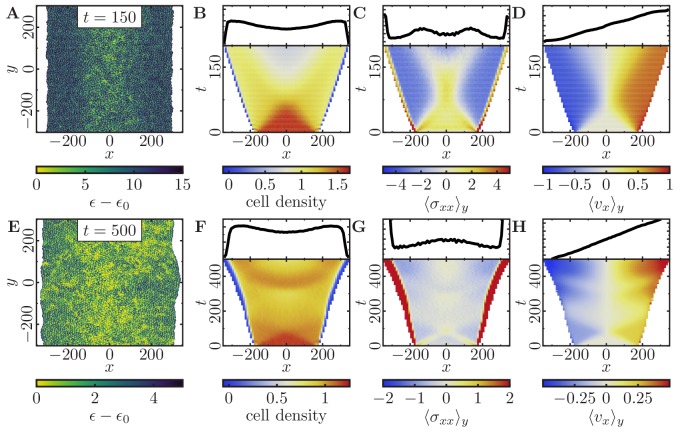
Figure 5. Expansion of a confluent epithelial cell sheet after removal of boundaries positioned at for two different parameter settings.
(Stiffness parameters , ; average polarization field ; signaling radius ; cytoskeletal update rate ; cell-cell adhesion ; cell-cell dissipation ; cell-substrate dissipation ; cell-substrate adhesion penalty ; independent simulations for each set of parameters). (A–D) Tissue expansion for a migration-dominated setup without explicit cell growth and mitosis. (-cell system; maximum cell polarity ). (E–H) Tissue expansion at low density and cell polarizability for a cell sheet comprised of dividing cells. (Initially a -cell system; maximum cell polarity ; growth time ; division time ; size threshold for cell growth , where is the size of a solitary cell in equilibrium). (A, E) Snapshots of the polarization field ; cf. Figure 5—video 1 and Figure 5—video 2. (B, F) Kymographs showing the cell density averaged over the -direction and (top) final snapshots of the cell density profiles. (C, G) Kymographs showing the component of the stress tensor averaged over the -direction and (top) final snapshots of the stress profiles. (D, H) Kymographs showing the component of the cell velocities averaged over the -direction and (top) final snapshot of the velocity profiles.