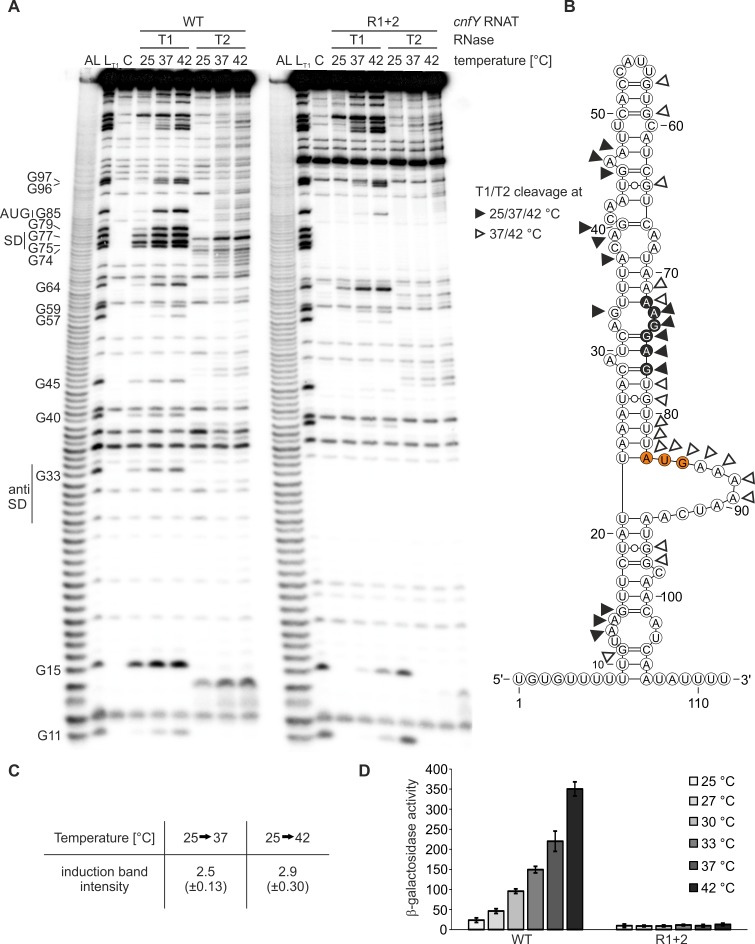
Fig 6. The cnfY RNAT undergoes a structural conversion in response to temperature.
(A) Enzymatic structure probing of the cnfY RNAT (wild type (WT, pBO4465)) and R1+2 variant (pBO4466)) at 25, 37 and 42°C. In vitro transcribed RNA was radiolabeled prior to enzymatic digestion with RNase T1 (0.0025 U) and RNase T2 (0.056 U) at the indicated temperatures. Lane L: alkaline ladder, lane LT1: RNase T1 cleavage in sequence buffer at 37°C, lane C: RNA treated with water instead of RNase served as control. (B) PARS-derived secondary structure of the cnfY RNAT [18] at 25°C. Nucleotides cleaved by RNase T1/T2 at all three temperatures or exclusively at 37 and 42°C are indicated. Nucleotides of the SD region and the AUG start codon are colored in black and orange, respectively. (C) Cleavage signals of the SD sequence (nucleotides G74, G75, and G77 cleaved by RNase T1) were quantified by integrated density quantification using AlphaEaseFC software. The mean density ratio (37°C/25°C) and its standard deviation was calculated from three independent experiments (biological replicate). (D) The wild type (WT; pBO4481) and R1+2 cnfY RNAT (pBO6507) were translationally fused to bgaB and reporter gene activity was measured as follows. E. coli DH5α cells harboring the corresponding plasmid (technical triplicate per each construct) were grown to an OD600 = 0.5 at 25°C. Afterwards, transcription was induced with 0.01% (w/v) L-arabinose and the culture was split. One sixth remained at 25°C while the other sixths were transferred into pre-warmed flasks at the indicated temperatures. After 30 min of incubation, samples were taken for subsequent β-galactosidase assay. The displayed results represent the mean activities from three independent experiments. Mean standard deviations are indicated as error bars.