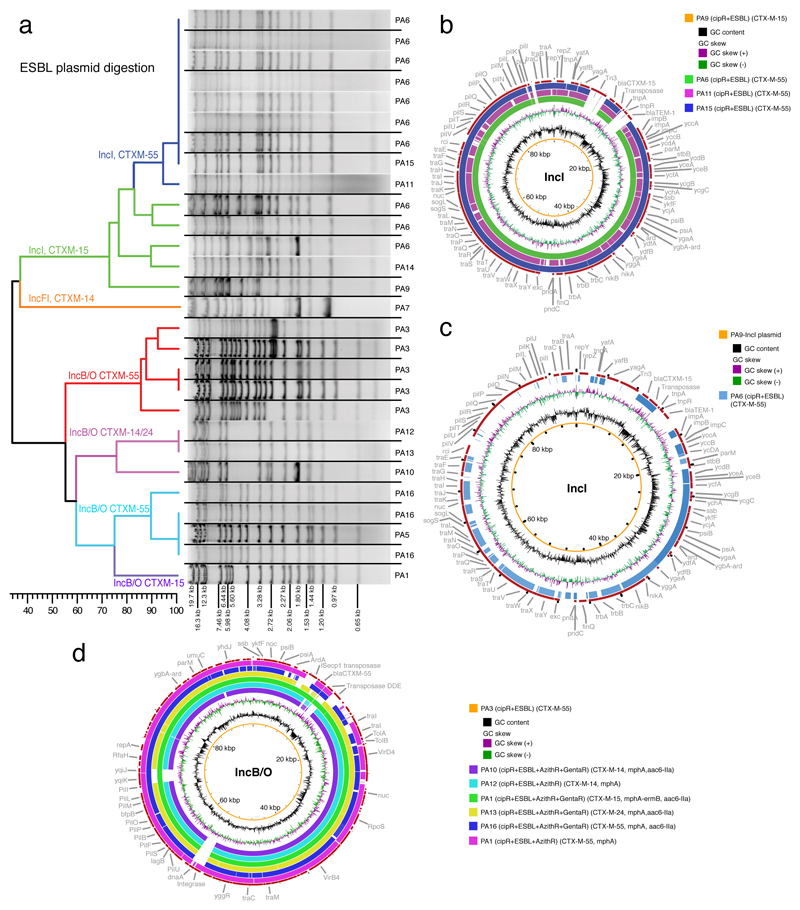
Figure 2. The diversity of ESBL-encoding plasmids in ciprofloxacin-resistant Shigella sonnei.
a) Dendrogram showing the similarities in restriction digestion patterns of ESBL-encoding plasmids associated with independent plasmid acquisitions. Black lines separate lanes that were not contiguous in a gel. Data were obtained from a single experiment. b) BLAST comparisons of IncI plasmids associated with four independent acquisitions (PA6, 9, 11, 15). The central circle indicates the full reference sequence of the IncI plasmid associated with PA9, with similarity between the reference sequence and other IncI plasmids shown as concentric rings. c) BLASTN comparison between IncI and IncB/O plasmid structures, in which the central circle indicates the IncI plasmid (PA9). d) BLAST comparisons of IncB/O plasmids associated with seven independent acquisitions (PA1, 3, 5, 10, 12, 13, 16). The central circle indicates the full reference sequence of the IncB/O plasmid associated with PA3, with similarity between the reference sequence and other IncB/O plasmids shown as concentric rings.