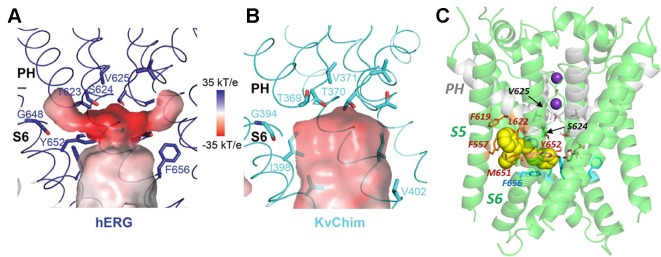
Figure 4.
Comparison of the hERG pore cavity (A) with that of the Kv1.2/2.1 channel chimera (KvChim) (B). The hERG cavity is smaller than the equivalent KvChim cavity and has hydrophobic “pockets” that project from the central cavity below the bottom of the selectivity filter and underneath the pore helix (PH). The pore helix negative dipole charges focus a strong negative electrostatic potential below the selectivity filter which contributes to the binding energy for positively-charged hERG pore blockers. (C) The hERG blocker “Cavalli-2” [(Cavalli et al., 2012); yellow space filling representation] can be docked partially within a hydrophobic pocket although readjustment of F656 side chains is required for interaction of blocker with more than one F656 side chain [see text; adapted from (Helliwell et al., 2018)]. Panels (A and B) from (Wang and MacKinnon, 2017) with permission.