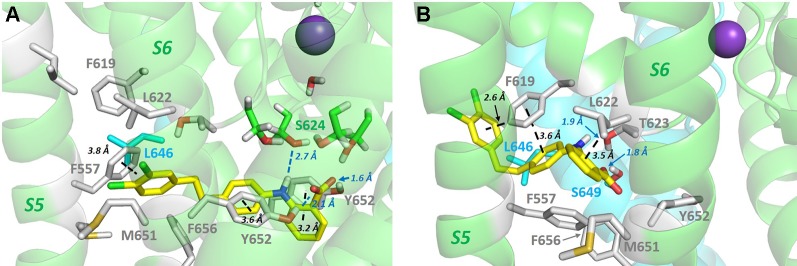
Figure 5.
(A) PD-118057 (yellow sticks) can be docked into the hERG structure in configurations that orient the benzyl carboxyl group to interact with K+ ions as they traverse the hERG conductance pathway as suggested in (Schewe et al., 2019). However in these configurations PD-118057 does not make favourable interactions with F619, L622 (and L646 on the adjacent subunit), identified as key binding determinants for this activator (Perry et al., 2009). Also PD-118057 would be expected to interact with Y652 and F557 in these states whereas mutagenesis of Y652 and F557 has minimal effect on activator binding (Perry et al., 2009). (B) Docked states consistent with mutagenesis (Perry et al., 2009) (aromatic stacking and van der Waals interactions with F619, L622 and adjacent L646 side chain) can be found deeper within the hydrophobic pockets below the pore helix, but these states are not compatible with interaction of the PD-118057 carboxylate with K+ ions in the pore as suggested in (Schewe et al., 2019). To orient the viewer, PD-118057 occupies a hydrophobic pocket similar to that shown in Figure 4C for Cavalli-2 binding, with the dichlorophenyl group (chlorine atoms green) of PD-118057 close to the membrane in panel B. Docking was performed with GOLD version 5.6; Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, Cambridge, UK as described previously (Dempsey et al., 2014; Helliwell et al., 2018).