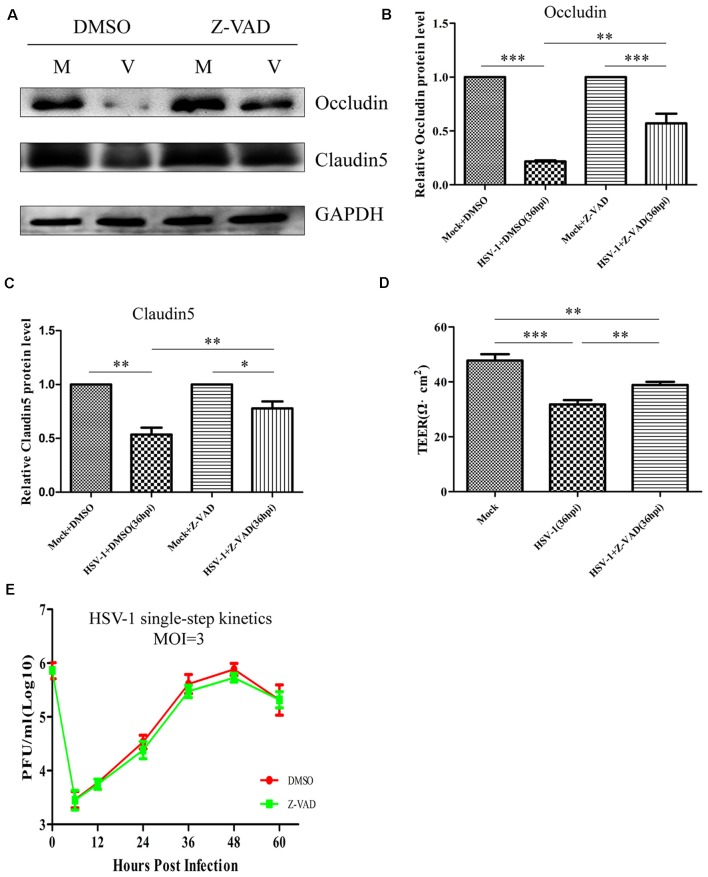
Figure 8.
Z-VAD-fmk improves endothelial cell barrier structure and function during HSV-1 infection. At 12 hpi, mock-infected (Mock) and HSV-1-infected (V) Bend.3 cells were treated with DMSO or Z-VAD-fmk (100 μM) and then harvested at 36 hpi. (A) Occludin and claudin 5 protein levels were determined by immunoblotting in HSV-1-infected cells treated with DMSO or Z-VAD-fmk and expressed as fold changes relative to mock-infected cells treated with DMSO or Z-VAD-fmk, respectively, after normalization to GAPDH levels. GAPDH serves as a loading control. Quantification of (A) is shown in (B,C). (D) Bend.3 barrier function was assayed by TEER measurements. The results show the barrier function of Bend.3 was improved by treatment with Z-VAD-fmk during HSV-1 infection. All data are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments and were analyzed by the Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (E) Growth kinetics of viruses. Bend.3 cells were infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 3. Supernatant samples from HSV-1-infected cells were collected at the indicated times post-infection. Prior to each sample collection, HSV-1-infected cells were preincubated with DMSO or Z-VAD-fmk (100 μM) for 24 h. Viral titer was measured with a plaque formation assay in triplicate. Data shown are presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments and were analyzed by two-way ANOVA.