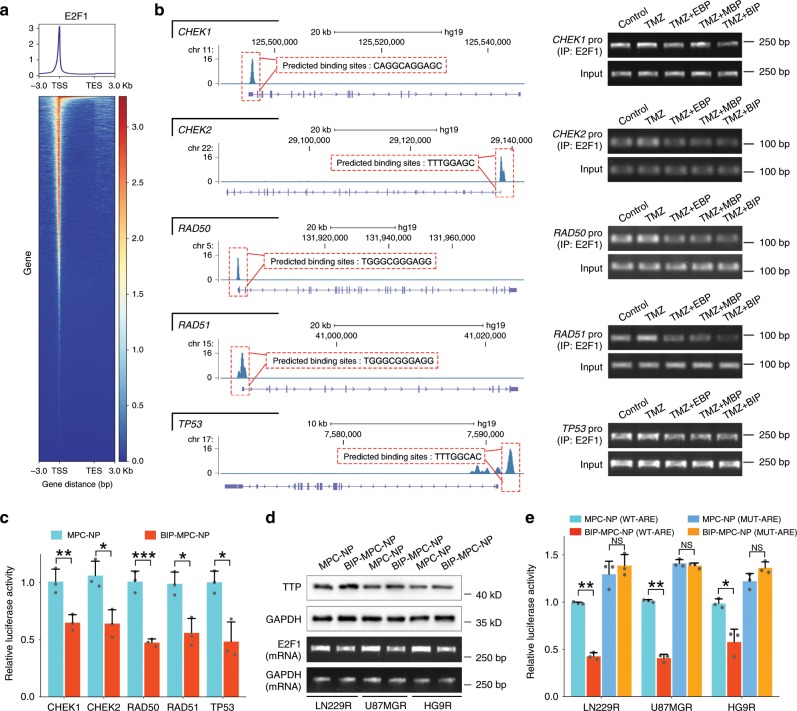
Fig. 5. BIP-MPC-NP restrains E2F1-mediated DNA damage repair modules via the inhibitory effect of TTP.
a E2F1 binding sites within a region spanning ± 3 kb around TSS in the whole genome. b The signal peaks located in the promoter regions of CHEK1, CHEK2, RAD50, RAD51 and TP53 in E2F1 ChIP-seq data and the binding sites of E2F1 were predicted on JASPAR datasets. The agarose gel electrophoresis displayed the enrichments of E2F1 in the promoter regions of CHEK1, CHEK2, RAD50, RAD51 and TP53 of LN229R. c The luciferase reporter assay displayed the E2F1 transcriptional activity in the promoter regions of CHEK1, CHEK2, RAD50, RAD51 and TP53 in LN229R (n = 3). d The TTP protein expression and E2F1 mRNA expression in LN229R, U87MGR and HG9R treated with MPC-NP or BIP-MPC-NP. e The inhibitory effect of TTP on wild-type or mutant-type ARE motifs within the E2F1 mRNA 3′-UTR in LN229R cells with MPC-NP or BIP-MPC-NP treatments (n = 3). The error bars in c and e represent the S.D. of three measurements. P value is determined by Student’s t-test. Significant results are presented as NS non-significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.