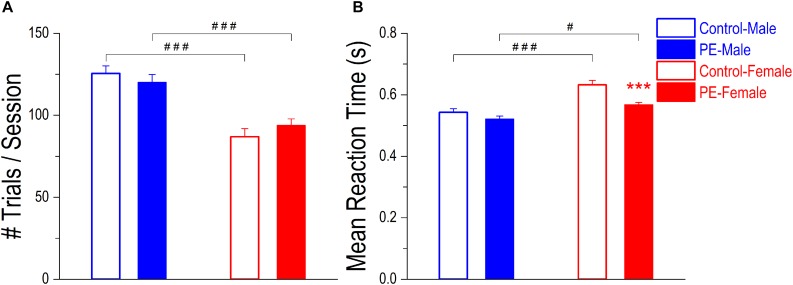
FIGURE 4.
Prenatal ethanol exposure (PE) did not lead to operant learning or motor deficits. (A) Operant learning was not impacted by PE. After training, no differences were observed in number of trials completed per session between control and PE rats of the same sex. In addition, male rats completed more trials/session than their female counterparts with or without PE. (B) Prenatal ethanol exposure did not cause observable motor deficits. There was no difference in mean reaction time between control and PE male rats. In females, PE rats had even shorter mean reaction time than controls. In addition, male rats responded more rapidly than females with or without PE. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, control vs. PE in females. #p < 0.05; ###p < 0.001, male vs. female with the same prenatal treatment.