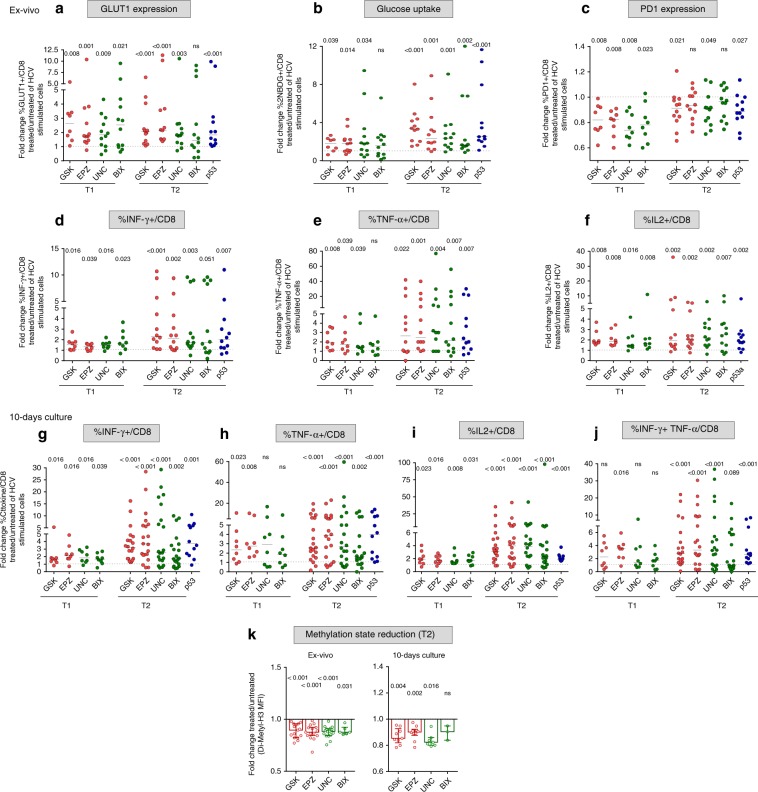
Fig. 7. HMT and p53 inhibitors improve anti-viral and metabolic functions of exhausted HCV-specific CD8+ T cells.
PBMC from chronically evolving (T1/early) or chronic (T2/late) HCV patients were stimulated for 40 h with HCV-NS3 peptides in the presence or absence of the EZH2 inhibitors GSK126 (GSK) and EPZ005687 (EPZ) (red dots), of the EHMT2/G9a inhibitors UNC0638 (UNC) and BIX01294 (BIX) (green dots), and of the p53 inhibitor pifithrin-alfa (p53) (blue dots). HCV-stimulated CD8+ T cells were then tested in flow cytometry for GLUT-1 levels (a), glucose uptake (b), PD-1 expression (c), IFN-γ (d), TNF-α (e), and IL2 (f) production. g–j PBMC from chronically evolving (T1/early) or chronic (T2/late) HCV patients were stimulated for 10 days with HCV-NS3 peptides in the presence or absence of the inhibitors specified in a and CD8+ T cells were then tested for IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL2, and IFN-γ plus TNF-α production as indicated. Data are presented as the ratio (fold-change) between positive CD8+ T cells detected in treated vs. untreated cultures from individual patients. Statistical analysis was performed with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test; horizontal lines represent median values. k Reduction of the repressive H3K9me2 histone mark was assessed by flow cytometry on CD8+ T cells from T2/late chronic HCV patients stimulated for 40 h or 10 days as in a. Data are presented as the ratio (fold-change) between MFI (Median fluorescence intensity) of H3K9me2 CD8+ T cells detected in treated vs. untreated cultures from individual patients; statistical analysis was performed with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test; columns and dots represent median values and single patients, respectively.