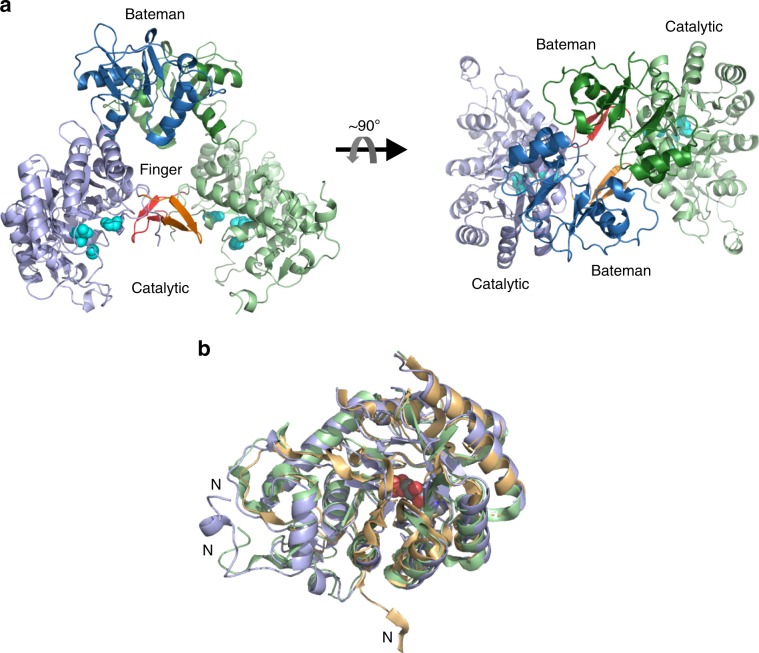
Fig. 4. Structure of TbIMPDH and catalytic domain comparison.
a Side and top view on the two monomers of TbIMPDH (green and blue), each consisting of the catalytic (light colors) and the regulatory Bateman domain (dark colors), that form a dimer in the ASU. The finger domains (red and orange) as well as the residues Asp358, Gly360, and Gly381 that are usually involved in hydrogen bond formation with the ribose and the phosphate moiety of IMP (cyan, in sphere representation) are highlighted. b Superposition of the catalytic domain of TbIMPDH (residues 8–120 and 237–514, blue) with corresponding residues of human IMPDH1 (PDB 1JCN, green), in complex with the substrate analog 6-chloropurine riboside 5′-monophosphate (CPR, in sphere representation) to locate the substrate binding site, and of the bacterial IMPDH from P. aeruginosa (PDB 1DQW, yellow). N N-terminus.