Figure 4. Scm3 Shows Chaperone-like Activity for Cse4/H4.
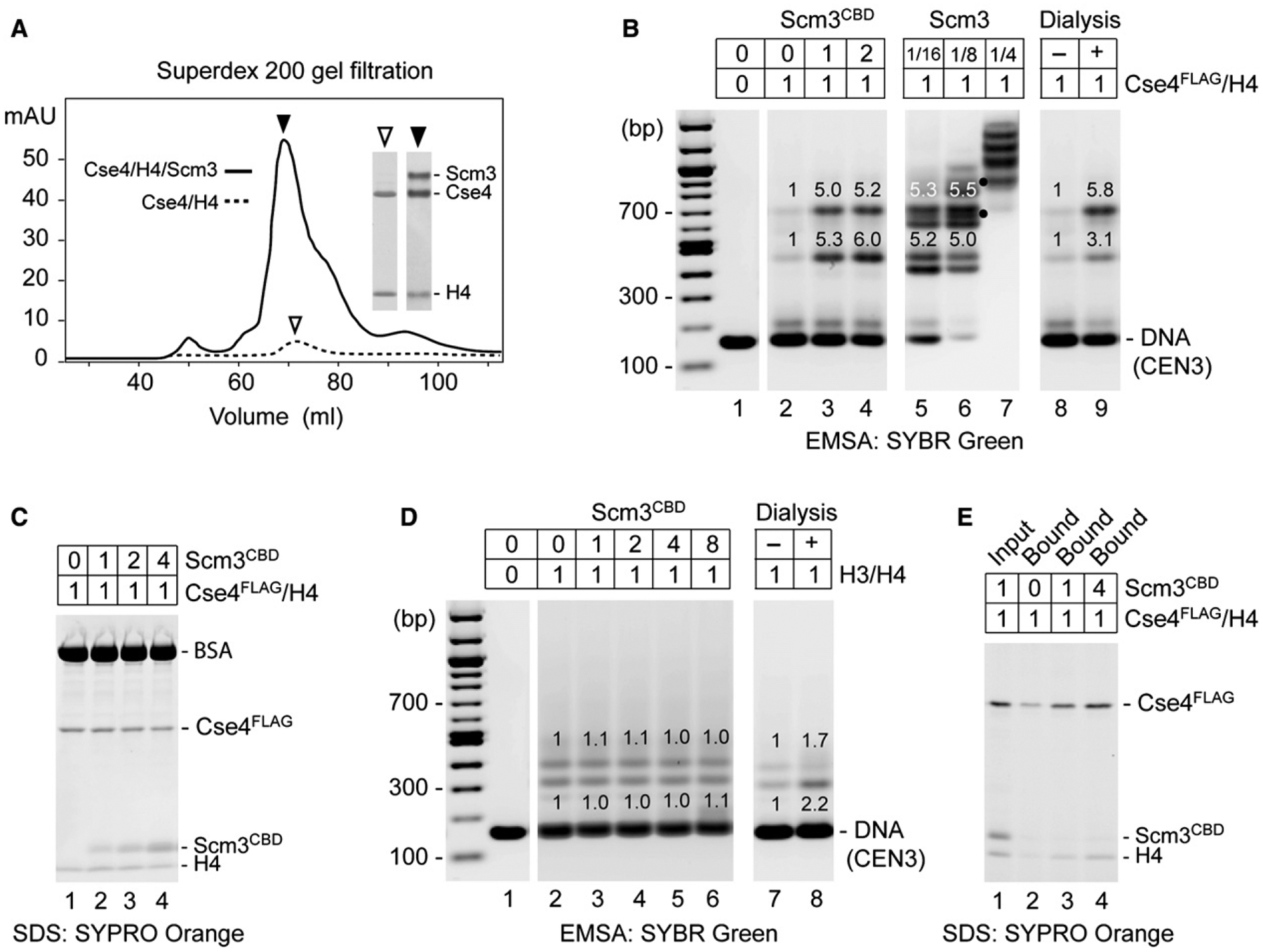
(A) Scm3 prevents loss of Cse4 and H4 during protein refolding and chromatography. Shown is Superdex 200 gel filtration of refolded Cse4/H4/Scm3 and Cse4/H4 complexes. Insets show SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining of protein peak fractions (2 μl for Cse4/H4/Scm3 fraction and 20 μl for Cse4/H4).
(B) Scm3CBD promotes loading of Cse4FLAG/H4 on CEN3 DNA. Proteins were abruptly diluted from 2.0M to 0.2M NaCl and incubated with DNA. EMSA shows binding of CEN3 DNA (0.5 μg) by Cse4FLAG/H4 (1.2 μg) in the presence of 0-, 1-, and 2-fold molar excess of Scm3CBD (lanes 2–4) and in the presence of full-length Scm3 (lanes 5–7 where dots mark distinctly resolved complexes that may contain both Scm3 and Cse4FLAG), as compared to salt dialysis (lanes 8 and 9). Relative fluorescence intensity is indicated above gel bands.
(C) SDS-PAGE of proteins that remained in solution after DNA binding reaction. Protein binding to CEN3 was performed as in (B).
(D) Scm3CBD has no effect on H3/H4 loading. Reactions with increasing molar ratios of Scm3CBD to H3/H4 were analyzed as in (B).
(E) Scm3CBD fails to stably associate with Cse4FLAG/H4 on DNA. Protein binding to biotin-labeled CEN3 was performed as in (B), in the presence of 0-, 1-, and 4-fold molar excess of Scm3CBD. DNA-bound proteins were pulled down with streptavidin-coated beads and analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
