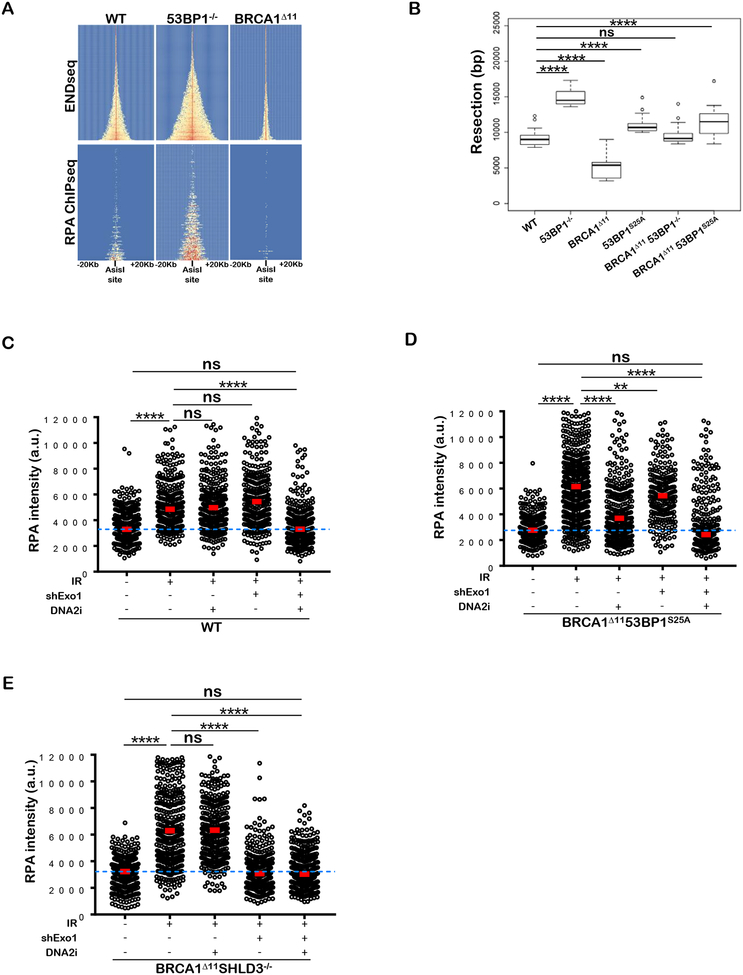
Figure 4. BRCA 1Δ1153BP1S25A cells exhibit normal levels of end resection catalyzed mainly by DNA2.
(A) Top panel: Heat map of END-seq signals across individual AsiSI sites in WT, 53BP1−/− and BRCA1Δ11 MEFs measured 5 hours after AsiSI induction. Lower panel: ChIP-seq for ssDNA bound by RPA in the same cells. Heat maps are ordered by END-seq signal intensity in WT cells. (B) Box plots showing quantification of resection end points in the top 10% resected breaks in WT, 53BP1−/−, BRCA1Δ11, 53BP1S25A, BRCA1An53BP1−/− and BRCA1Δ1153BP1S25A MEFs at AsiSI cleaved DSB sites. Welch’s t-test was used to determine statistical significance. (C) Quantification of the intensity of chromatin bound RPA in individual EdU-positive nuclei from WT and EXO1-depleted MEFs, either pre-treated or not with 1 μM DNA2i prior to 10 Gy IR. Cells were analyzed 4 hours post-IR. (D) Quantification of the intensity of chromatin bound RPA in individual EdU-positive nuclei from EXO1-proficient and EXO1-depleted BRCA1Δ1153BP1S25A MEFs, either pre-treated or not with 1 μM DNA2i prior to 10 Gy IR. Cells were analyzed 4 hours post-IR. (E) Quantification of the intensity of chromatin bound RPA in individual EdU-positive nuclei from EXO1-proficient and EXO1-depleted BRCA1Δ11SHLD3−/− MEFs, either pre-treated or not with 1 μM DNA2i prior to 10 Gy IR. Cells were analyzed 4 hours post-IR. In panels C, D, and E a minimum of 300 nuclei per condition were quantified using the Gen5 spot analysis software. A representative experiment (n=2) is shown. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney t-test.