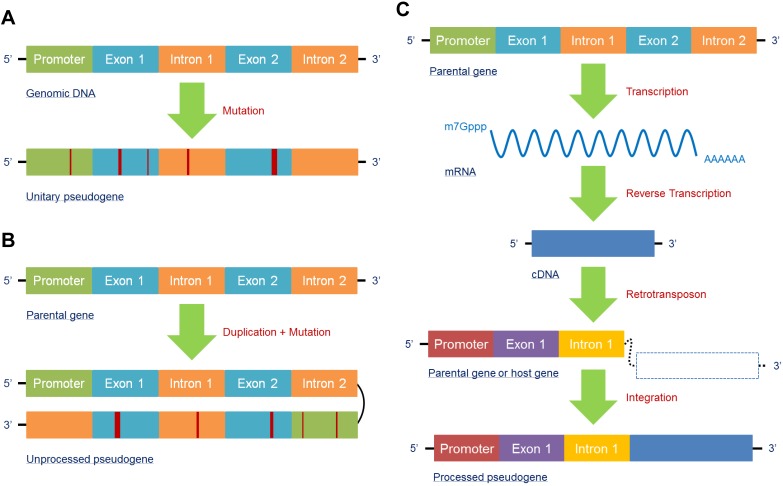
Figure 1.
Pseudogenes are mainly generated in three forms. (A) The unitary pseudogene is derived from a coding gene with several mutations involved, leading to loss of its transcription and translation capacities, with have no fully functional counterpart in the same genome. (B) Due to unfaithful duplication, the duplicated gene generates a mutated gene copy that eventually becomes an unprocessed pseudogene; the original gene copy is fully functional. (C) A processed pseudogene derives from an mRNA that has been reverse transcribed into a cDNA and then synthesized into a host gene or parental gene via retrotransposon. Processed pseudogenes can be found far from their counterparts or on different chromosomes.