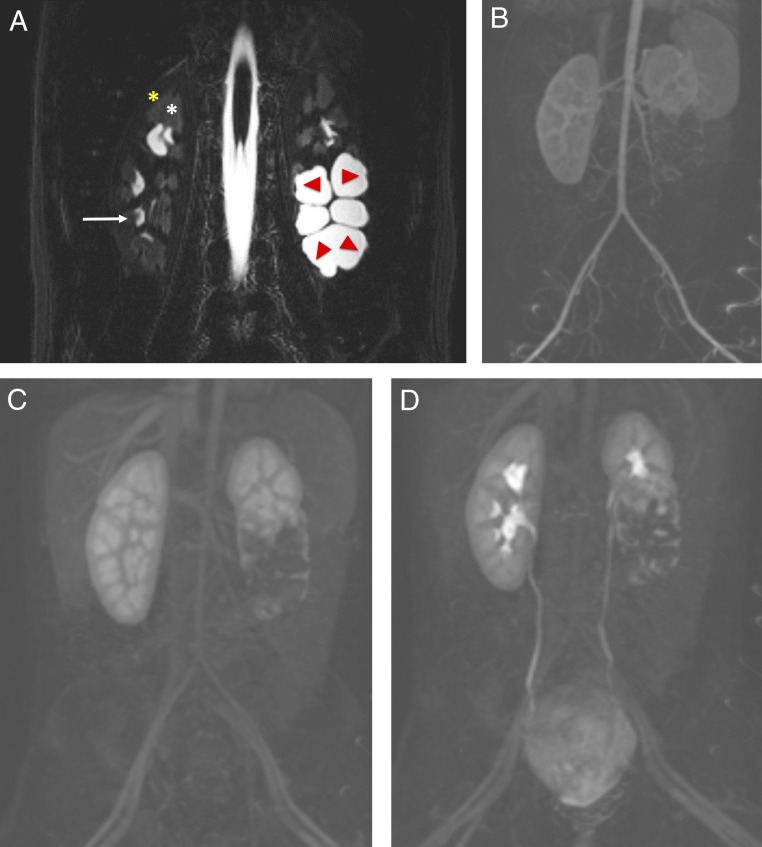
FIGURE 12.
Renal anatomy as seen in MRU. A, Coronal fluid-sensitive (heavily T2-weighted) MR image reveals a normal right kidney with low-signal intensity of the cortex (yellow star), intermediate-signal intensity of the medulla (white star) and high intensity (urine) within the normal calyces (white arrow). The left kidney has a duplicated collecting system with markedly dilated central calyces in the lower pole, which is obstructed (red arrows). B–D, Coronal dynamic subtracted postcontrast T1-weighted MR images reveal the transit of contrast from the aorta and cortex, to the medullary renal parenchyma, and into the collecting system, including delineation of the normal ureters and bladder, which is normal in the right kidney and upper pole of the left kidney but incomplete and delayed of the abnormal left lower moiety.