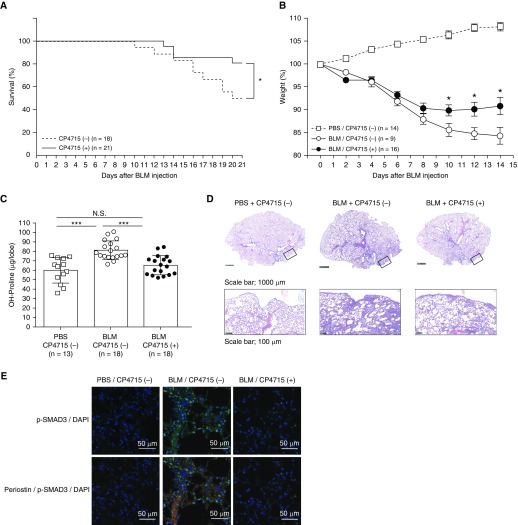
Figure 6.
Effect of CP4715 on BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Nine-week-old C57BL/6 mice and periostin-deficient (Postn−/−) mice or their heterozygous littermates (Postn+/−) weighing less than 28.5 g were used. Postn−/− mice were prepared as previously described (11). Murine lung fibrosis was induced by a single administration of 3 mg/kg of BLM via the oropharyngeal aspiration route on Day 0. Two osmotic pumps filled with 200 μl of CP4715 (50 mg/ml) or an equal volume of vehicle (50% DMSO) were subcutaneously implanted into C57BL/6 mice at 5 days before BLM instillation, and CP4715 was released at 0.5 μl/h. (A–E) The mortality (A) and weight loss (B) of the mice were evaluated 3 weeks or 2 weeks after BLM administration, respectively, and hydroxyproline measurement (C), Masson trichrome staining (D), and immunostaining with indicated antibodies (E) were performed on Day 10. In D, the upper and lower lines represent low and high magnifications, respectively. The boxes represent the portions shown in the high magnifications. Scale bars: 1,000 μm and 100 μm. In E, the photographs of phosphorylated Smad3 (green) and DAPI (blue) with or without periostin (red) have been merged. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. Scale bars: 50 μm.