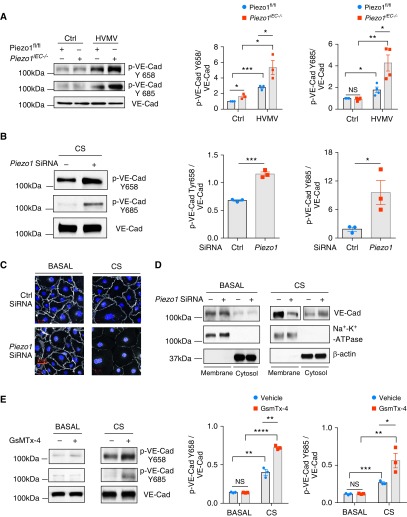
Figure 2.
Loss of Piezo1 in ECs augments HVMV-induced vascular endothelial cadherin (VE-Cad) phosphorylation and disruption of adherens junctions (AJs) in lung endothelium. (A) Western blot analysis of VE-Cad phosphorylation in lungs of Piezo1fl/fl and Piezo1iEC−/− mice after mechanical ventilation with tidal volume of 40 ml/kg for 30 minutes. Piezo1iEC−/− increases HVMV-induced phosphorylation of VE-Cad at Y658 and Y685. Mean ± SEM; n = 3–4. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by ANOVA. (B) Western blot analysis of VE-Cad phosphorylation in HLMVEC monolayers after 18% cyclic stretch (CS) for 30 minutes. Depletion of Piezo1 by siRNA increases stretch-induced phosphorylation of VE-Cad at Y658 and Y685 as compared with scrambled siRNA-treated cells. Mean ± SEM; n = 3. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed t test. (C) Confocal imaging of VE-Cad (white) and nuclei (DAPI; blue) of HLMVEC monolayers transfected with scrambled or Piezo1 siRNA under basal static conditions and after 30 minutes of 18% CS. Scale bars: 20 μm. (D) Distribution of VE-Cad between plasma membrane and cytosolic pool by Western blot analysis in HLMVEC monolayers transfected with scrambled or Piezo1 siRNA under basal static conditions and after 30 minutes of 18% CS. Depletion of Piezo1 decreased membrane VE-Cad expression and increased cytosolic pool. (E) Western blot analysis of VE-Cad phosphorylation in HLMVEC monolayers treated with 500 nM GsmTx-4 or vehicle control under basal static conditions and after 30 minutes of 18% CS. Pharmacological inhibition of Piezo1 channels increases phosphorylation of VE-Cad at Y658 and Y685. Mean ± SEM; n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by two-tailed t test. HLMVEC = human lung microvascular endothelial cell.