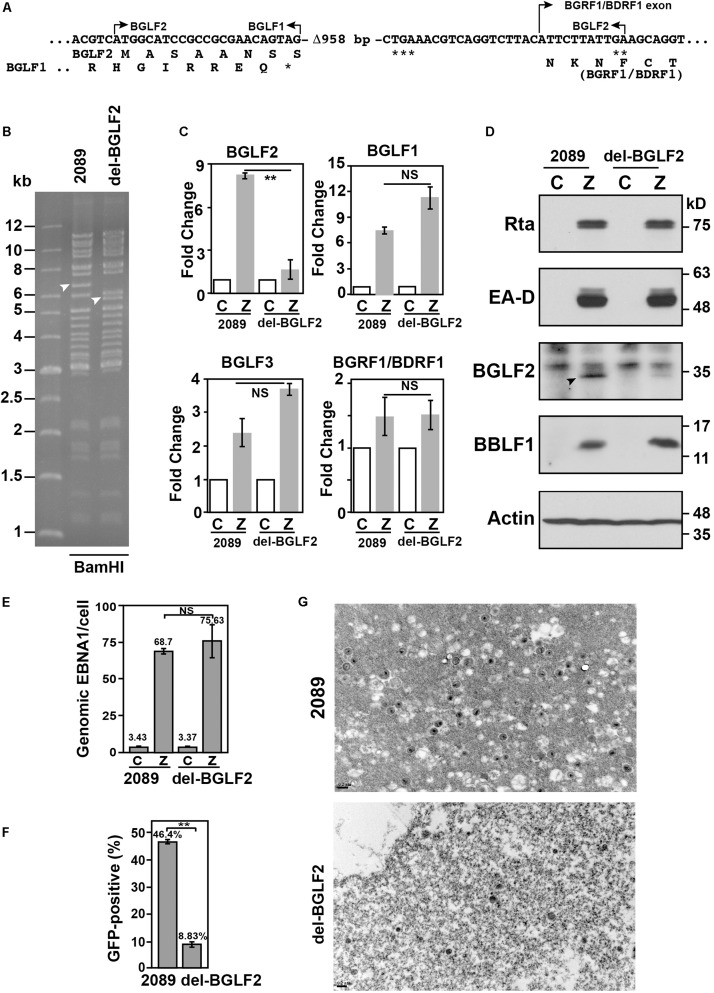
FIGURE 6.
Influence of BGLF2 and Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) maturation. (A) Sequence of del-BGLF2. del-BGLF2 was generated by deleting an internal 958-bp sequence (Δ-958) in BGLF2. The deletion caused a premature termination at a termination codon that is indicated by ***. ** Indicates the termination codon of BGLF2. * indicates the termination codon of BGLF1. The amino acids encoded by the genes are shown below the DNA sequence. Arrows indicate the start and the end of an open reading frame, or BGRF1 exon. (B) p2089 and del-BGLF2 bacmid DNA were digested with BamHI, and restriction fragments were analyzed with a 0.6% agarose gel. Arrowheads indicate the DNA fragment containing the BGLF2 sequence. (C) The expressions of BGLF1, BGLF2, BGLF3, and BGRF1/BDRF1 in HEK293 (2089) and HEK293 (del-BGLF2) were determined by RT-qPCR 24 h post-transfection. The relative expression of each gene in cells transfected with pCMV-Zta (Z) was normalized to the amount of GAPDH and expressed as the fold change relative to that cell transfected with empty vector (C). (D) At 72 h post-transfection, Rta, EA-D, BGLF2, BBLF1, and α-actin in the cell lysate were analyzed by immunoblotting. (E) The amount of EBV DNA in the cell lysates was analyzed by qPCR and was normalized to the number of copies of a cellular gene, PIK3CA. (F) Raji cells were infected with virus particles that were released by HEK293 (p2089) and HEK293 (del-BGLF2) cells after lytic induction by transfecting cells with pCMV-Zta. The percentage of Raji cells that were GFP-positive was determined by FACS analysis. The experiments were conducted three times, and the results were analyzed statistically using the t-test. **p < 0.01; NS, not statistically significant. (G) Electron micrographs of pelleted viral particles that were released by HEK239 (2089) and HEK293 (del-BGLF2) transfected with pCMV-Zta.